Windows 10 Vs 11 Ram Usage
windows 10 vs 11 ram usage
Related Articles: windows 10 vs 11 ram usage
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to windows 10 vs 11 ram usage. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 vs. 11: A Comparative Analysis of RAM Usage

The ongoing debate surrounding Windows 10 and Windows 11 often centers around performance, with RAM usage being a key factor. This article delves into the intricacies of RAM consumption by both operating systems, providing a comprehensive analysis that sheds light on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding RAM and Its Significance
Random Access Memory (RAM) is the computer’s short-term memory. It stores data that the processor actively uses, enabling fast access and smooth operation. When a computer runs out of RAM, it begins using the hard drive as a temporary storage space, significantly slowing down performance. This phenomenon is known as "paging," and it’s a clear indicator that the system is struggling to keep up with demands.
Windows 10: A Legacy of Optimization
Windows 10, released in 2015, has undergone numerous optimizations and updates throughout its lifespan. This continuous development has resulted in a generally efficient operating system, capable of managing RAM effectively. However, the amount of RAM required for optimal performance can vary depending on the specific hardware configuration, installed applications, and user habits.
Windows 11: A New Era of Efficiency
Windows 11, launched in 2021, boasts a refined architecture designed to enhance performance and resource management. Microsoft introduced several features aimed at optimizing RAM usage, including:
- DirectStorage: This technology enables games to load assets directly from the storage device, bypassing the CPU and reducing RAM requirements.
- Windows Subsystem for Android: The integration of Android apps into Windows 11 minimizes RAM overhead by efficiently managing virtualized environments.
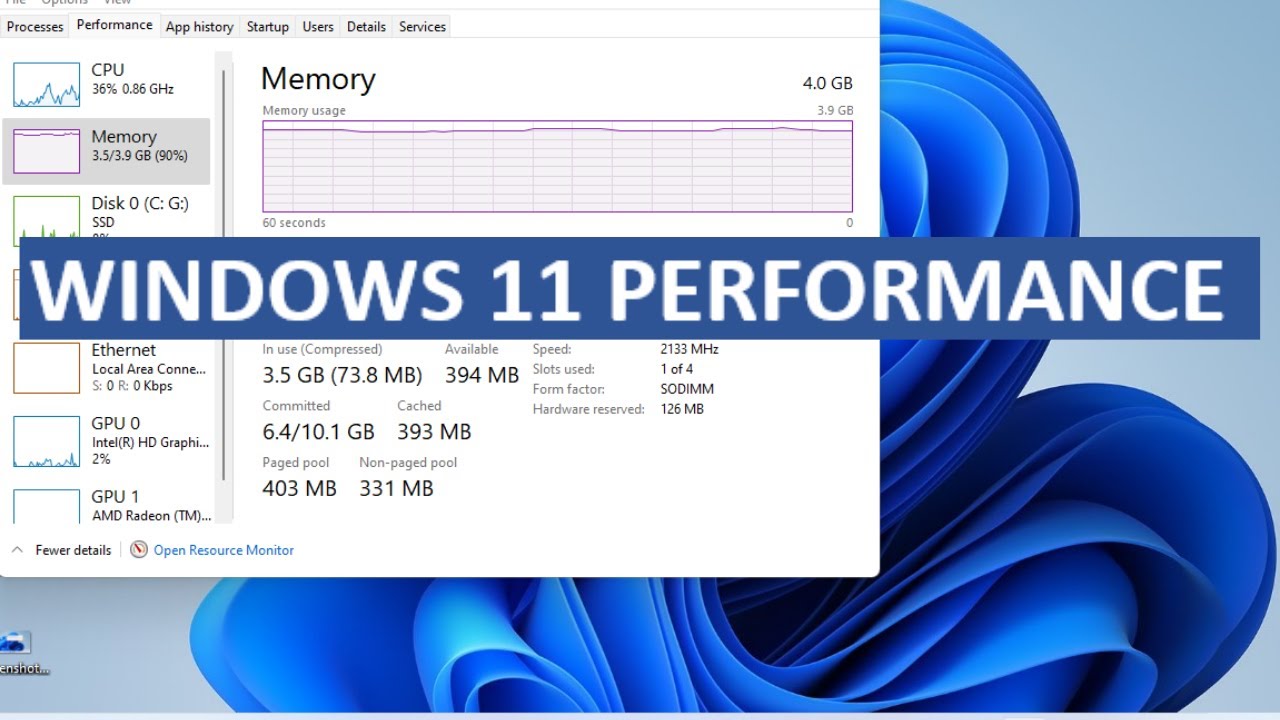
- Improved Task Manager: The Task Manager provides more granular insights into RAM usage, facilitating better resource allocation and troubleshooting.
Comparative Analysis: A Deeper Dive
To understand the nuances of RAM usage in Windows 10 and Windows 11, it’s essential to examine specific scenarios:
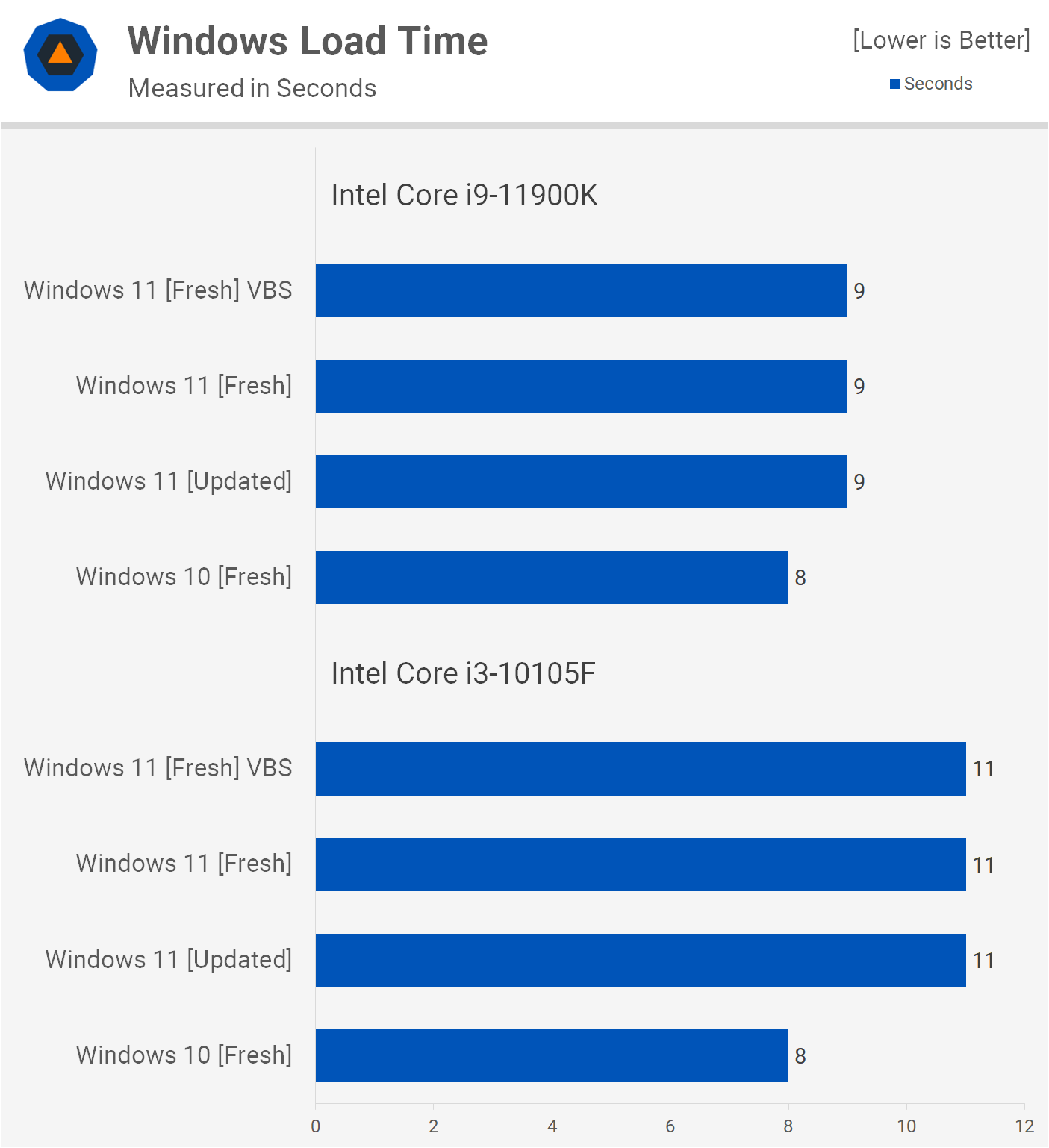
- Idle State: Both operating systems exhibit similar RAM usage when idle. However, Windows 11 may consume slightly more due to its additional features and background processes.
- Light Usage: When performing basic tasks like web browsing, document editing, and light multitasking, both operating systems generally manage RAM efficiently. Windows 11’s optimizations may offer a slight edge in resource management.
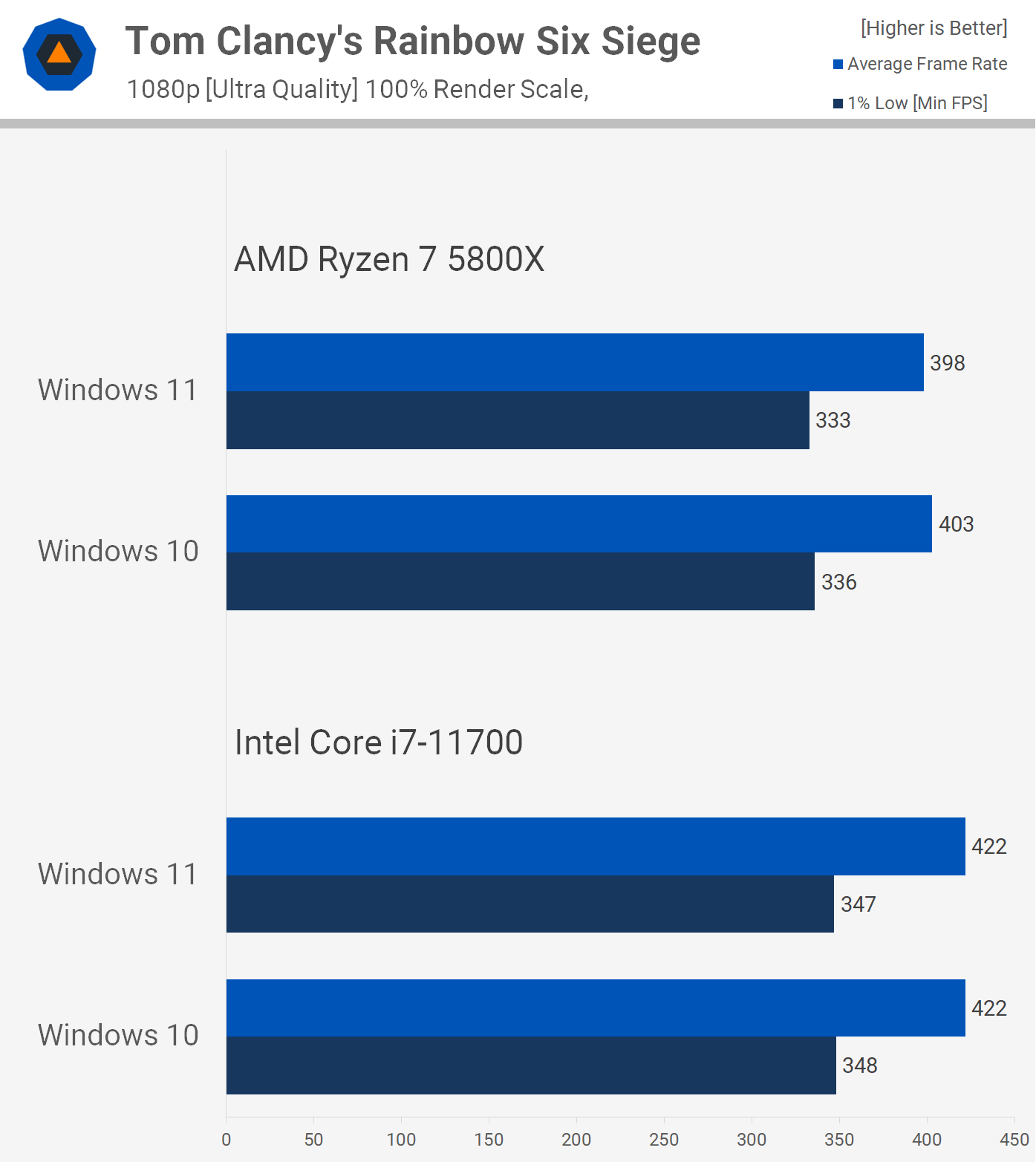
- Heavy Usage: Under demanding conditions, such as gaming, video editing, or running multiple resource-intensive applications, the differences in RAM usage become more pronounced. Windows 11’s DirectStorage and other optimizations can significantly reduce the overall RAM footprint compared to Windows 10.
Factors Influencing RAM Usage
While the operating system plays a crucial role in RAM management, several other factors contribute to its consumption:
- Hardware: The amount of RAM installed in the system directly impacts its available resources.
- Applications: Resource-hungry applications, such as games, video editing software, and web browsers with numerous extensions, can consume substantial RAM.
- Background Processes: System processes, background services, and installed applications running in the background contribute to overall RAM usage.
- User Habits: Frequent multitasking, opening multiple tabs in the browser, and running unnecessary programs can lead to increased RAM consumption.
Tips for Optimizing RAM Usage
Both Windows 10 and Windows 11 offer tools and settings to enhance RAM management:
- Task Manager: Monitor running processes and identify resource-intensive applications.
- Startup Programs: Disable unnecessary programs from launching automatically at startup.
- Background Processes: Limit the number of background processes and services running.
- Disk Cleanup: Regularly clean up temporary files and unnecessary data to free up disk space and improve performance.
- RAM Upgrades: Consider upgrading to a higher capacity RAM module to provide more resources for demanding applications.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Does Windows 11 require more RAM than Windows 10?
A: While Windows 11’s minimum system requirements are slightly higher than Windows 10, the actual RAM usage can vary based on the factors mentioned above. In general, both operating systems can perform well with 8GB of RAM for everyday tasks. However, for demanding workloads, 16GB or more is recommended.
Q: Which operating system is more efficient in managing RAM?
A: Windows 11 generally exhibits better RAM management due to its refined architecture and optimizations. However, the actual performance difference may be subtle in everyday use.
Q: How can I determine if my computer is using too much RAM?
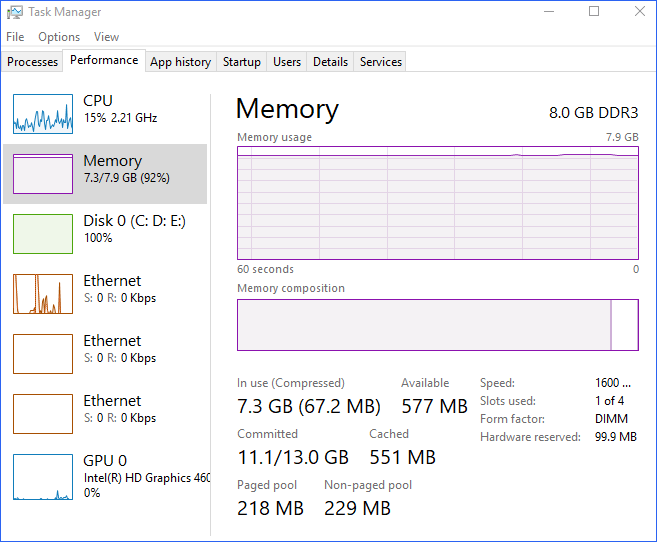
A: Monitor the Task Manager for high RAM usage, especially when experiencing slowdowns or application crashes. If the RAM usage consistently approaches or exceeds the available capacity, consider upgrading to a higher capacity module or optimizing resource usage.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective
While Windows 11 introduces optimizations designed to improve RAM management, both operating systems provide a solid foundation for efficient resource utilization. Ultimately, the optimal choice depends on individual needs and preferences. By understanding the factors influencing RAM usage and implementing appropriate optimization techniques, users can ensure smooth performance and a seamless computing experience on both Windows 10 and Windows 11.

![[OLD] Not Relevant!!! windows 11 vs windows 10 ram usage использование ОЗУ Gaming Performance](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_IjkVw6in4Y/maxresdefault.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into windows 10 vs 11 ram usage. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!