Windows 10 Vs 11 Performance On Old Hardware
windows 10 vs 11 performance on old hardware
Related Articles: windows 10 vs 11 performance on old hardware
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to windows 10 vs 11 performance on old hardware. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 vs. 11: Navigating Performance on Older Hardware
The evolution of operating systems is a constant dance between innovation and compatibility. While new features and enhanced security measures are undeniably appealing, the question of performance on older hardware often arises. This is particularly relevant when considering the transition from Windows 10 to Windows 11, a significant upgrade that brings notable changes in both design and functionality.
This article delves into the performance differences between Windows 10 and Windows 11 on older hardware, exploring the factors that contribute to potential performance discrepancies and providing insights to aid in decision-making.
Windows 10: A Familiar Foundation
Windows 10, released in 2015, has enjoyed widespread adoption and established itself as a robust and reliable operating system. Its compatibility with a vast range of hardware, including older systems, has been a significant factor in its success.
Windows 11: A New Era, New Requirements
Windows 11, launched in 2021, introduced a redesigned user interface, improved security features, and performance enhancements. However, this modernization came with a set of minimum hardware requirements that, unfortunately, excluded some older systems. This raised concerns about the impact on existing hardware and whether older machines could handle the new OS effectively.
Performance Considerations: A Detailed Examination
Understanding the performance differences between Windows 10 and Windows 11 on older hardware requires considering various factors:
1. Hardware Requirements:
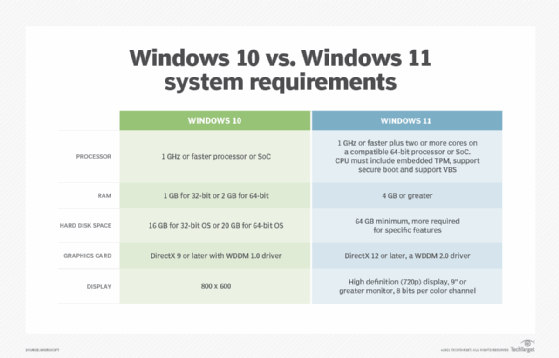
Windows 11’s minimum system requirements include a processor from the 8th generation Intel Core or AMD Ryzen 2000 series or newer, at least 4GB of RAM, and a 64GB storage drive. Older hardware that falls short of these requirements may struggle to run Windows 11 smoothly.
2. System Resources:
Windows 11’s visually appealing user interface and new features, while visually impressive, are resource-intensive. Older hardware, often equipped with limited RAM and slower processors, may experience slower loading times, lag, and overall performance degradation.
3. Software Compatibility:
While Windows 11 aims to maintain compatibility with existing software, some older programs may encounter issues or require updates to function optimally. This is a crucial factor to consider, especially if your work or personal activities rely on specific legacy software.
4. Driver Support:
Older hardware may not have readily available drivers for Windows 11. This lack of drivers can lead to hardware malfunctions, instability, and performance issues.
5. Security Updates:
Windows 10 will continue to receive security updates until October 14, 2025, while Windows 11 will receive updates for a longer period. This extended support for Windows 11 offers a significant advantage in terms of security and stability, particularly for older hardware that may be vulnerable to vulnerabilities.
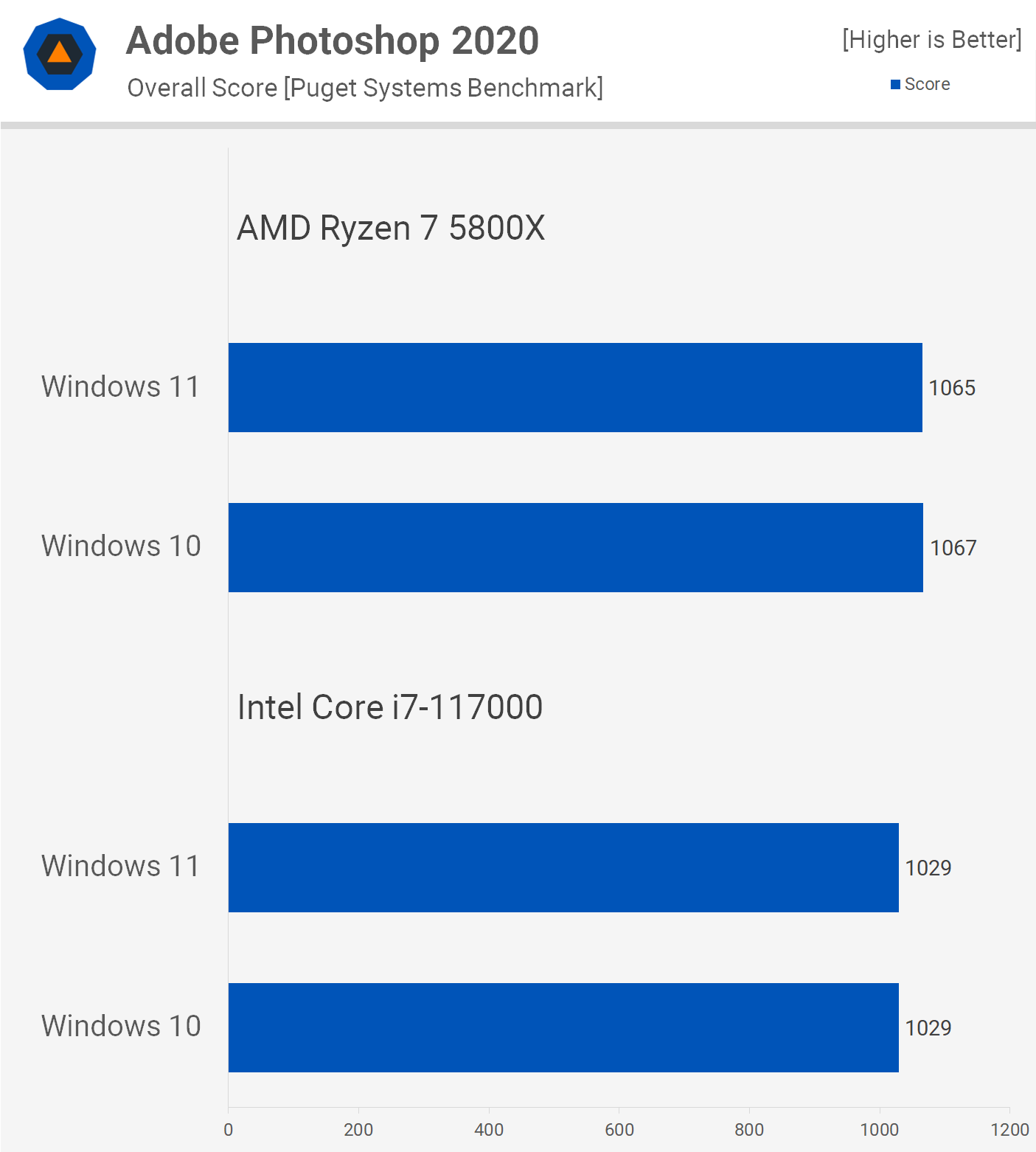
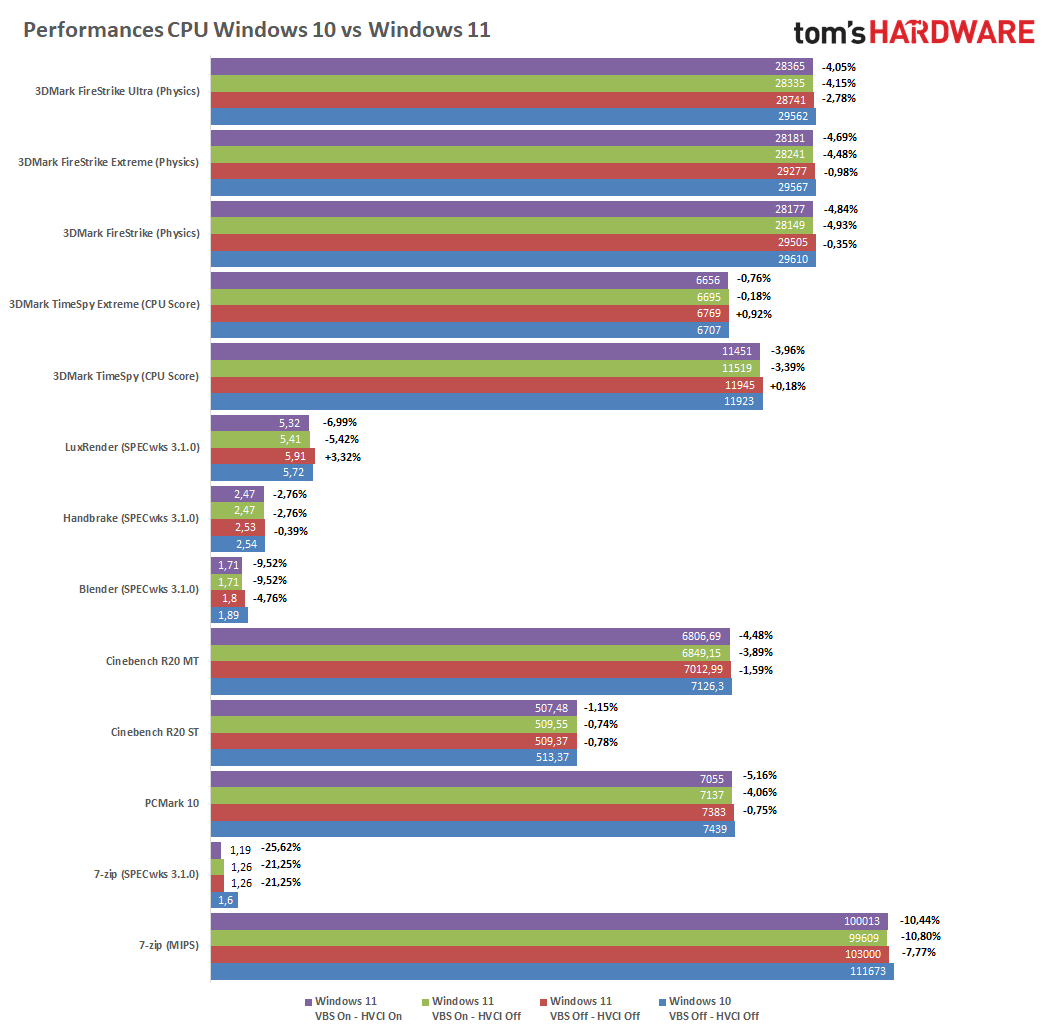
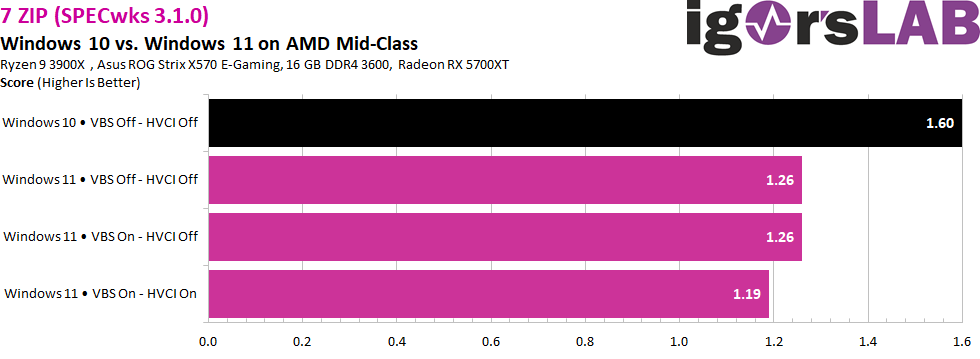
Performance Benchmarks: A Comparative Analysis
To provide a tangible understanding of the performance differences, several benchmarks can be used to compare Windows 10 and Windows 11 on older hardware. However, it’s important to note that these benchmarks are not definitive and can vary depending on the specific hardware configuration.
1. Boot Time:
Windows 11 often boasts faster boot times compared to Windows 10. This can be attributed to optimized system startup processes and improved hardware utilization. However, on older hardware with slower storage drives and processors, the difference in boot times may be negligible.
2. Application Launch Speed:
Windows 11 generally exhibits faster application launch times, particularly for newer applications designed for its architecture. However, older software may experience slower launch speeds due to compatibility issues or resource limitations.
3. Multitasking Performance:
Windows 11’s multitasking capabilities are generally improved, thanks to its optimized memory management and resource allocation. However, on older hardware with limited RAM, multitasking can still lead to noticeable performance degradation, including slowdowns and application crashes.
4. Graphics Performance:
Windows 11 features updated graphics drivers and support for DirectX 12 Ultimate, which can enhance gaming performance on newer hardware. However, on older hardware with outdated graphics cards, the performance difference may not be significant.
5. Battery Life:
Windows 11 includes power management enhancements that can improve battery life on newer devices. However, on older hardware with aging batteries, the impact on battery life may be minimal.
Factors Influencing Performance: A Deeper Dive
Beyond the general comparisons, several specific factors can significantly influence performance on older hardware:
1. CPU and RAM:
The processor and RAM are crucial components that directly impact system performance. Older hardware with slower CPUs and limited RAM will struggle to handle the demands of Windows 11.
2. Storage Drive:
The type and speed of the storage drive play a significant role in boot times, application loading speeds, and overall system responsiveness. Older hardware with slower hard disk drives (HDDs) will experience noticeable performance degradation compared to newer systems with solid-state drives (SSDs).
3. Graphics Card:
The graphics card is essential for visual performance, especially for gaming and multimedia applications. Older hardware with outdated graphics cards may struggle to run demanding games or applications smoothly.
4. Drivers and Updates:
Outdated or incompatible drivers can significantly impact performance. Ensuring that all hardware drivers are up-to-date is crucial for optimal performance, particularly on older hardware.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
1. Can I upgrade my older computer to Windows 11?
While Windows 11 has minimum hardware requirements, you may still be able to install it on older hardware that doesn’t meet those requirements. However, be aware that performance may be significantly degraded, and certain features may not function correctly.
2. Will Windows 11 run faster than Windows 10 on my older computer?
It’s unlikely that Windows 11 will run faster than Windows 10 on older hardware. In fact, it’s more likely that you’ll experience a performance decline due to the increased resource demands of Windows 11.
3. What are the risks of upgrading to Windows 11 on older hardware?
The risks of upgrading to Windows 11 on older hardware include:
- Performance degradation: You may experience slower boot times, application launch speeds, and overall responsiveness.
- Software compatibility issues: Some older software may not be compatible with Windows 11.
- Hardware malfunctions: Older hardware may not have compatible drivers for Windows 11, leading to instability and malfunctions.
4. Should I stick with Windows 10 or upgrade to Windows 11?
The decision to stick with Windows 10 or upgrade to Windows 11 depends on your specific needs and hardware configuration. If your hardware meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11 and you’re looking for new features and security enhancements, then upgrading may be worthwhile. However, if your hardware is older and you’re concerned about performance, it’s best to stick with Windows 10.
Tips for Optimizing Performance on Older Hardware
1. Upgrade RAM:
Increasing RAM is one of the most effective ways to improve performance on older hardware. More RAM will allow the system to run more applications simultaneously without slowing down.
2. Replace Hard Drive with SSD:
Upgrading from a hard disk drive (HDD) to a solid-state drive (SSD) can significantly boost boot times, application loading speeds, and overall system responsiveness.
3. Update Drivers:
Ensure that all hardware drivers are up-to-date. Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to performance issues and instability.
4. Uninstall Unnecessary Software:
Remove any software that you don’t use regularly, as it can consume system resources and slow down performance.
5. Disable Visual Effects:
Windows 11’s visually appealing effects can be resource-intensive. Consider disabling some of these effects to improve performance, especially on older hardware.
6. Use a Lightweight Antivirus:
Heavy antivirus programs can consume system resources and slow down performance. Consider using a lightweight antivirus that doesn’t impact performance as significantly.
7. Defragment Hard Drive:
Defragmenting a hard disk drive can improve performance by organizing files more efficiently. However, this is less relevant for SSDs, which don’t require defragmentation.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective
The choice between Windows 10 and Windows 11 on older hardware is a nuanced one, requiring careful consideration of performance implications. While Windows 11 offers a modern interface, improved security, and performance enhancements, its resource demands may pose challenges for older systems. Windows 10, with its established compatibility and ongoing security updates, remains a viable option for those seeking a stable and familiar experience.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to individual needs and priorities. If performance is a primary concern, sticking with Windows 10 may be the better choice. However, if you’re willing to sacrifice some performance for newer features and security, Windows 11 might be worth exploring.
Regardless of the operating system chosen, optimizing performance on older hardware through hardware upgrades, software optimization, and driver updates can significantly enhance the user experience.


![[OLD] Not Relevant!!! windows 11 vs windows 10 ram usage использование ОЗУ Gaming Performance](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_IjkVw6in4Y/maxresdefault.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into windows 10 vs 11 performance on old hardware. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!