Windows 10 Versus Windows Server
windows 10 versus windows server
Related Articles: windows 10 versus windows server
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to windows 10 versus windows server. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 vs. Windows Server: A Comprehensive Comparison
The Windows operating system reigns supreme in the realm of personal computing, with Windows 10 dominating the desktop and laptop landscape. However, when it comes to the enterprise, a different breed takes the stage: Windows Server. While both share a lineage, their roles and functionalities diverge significantly, catering to distinct user needs and environments. This article delves into the key differences between Windows 10 and Windows Server, shedding light on their strengths, limitations, and optimal use cases.
Core Purpose and Target Audience:
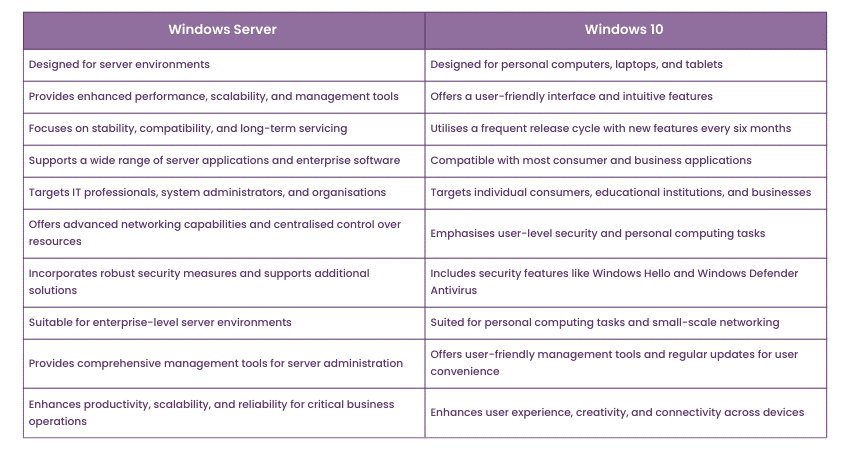
Windows 10 is designed for individual users and small businesses. It provides a user-friendly interface, robust security features, and access to a vast ecosystem of applications. Its focus lies on delivering a seamless and efficient user experience for everyday tasks, entertainment, and productivity.
Windows Server, on the other hand, is tailored for large organizations and data centers. It acts as a robust platform for managing networks, hosting applications, and storing data. It prioritizes stability, scalability, and security, enabling businesses to manage critical infrastructure and provide reliable services to users.
Key Differences:
1. Licensing and Cost:
- Windows 10: Licensed on a per-device basis, with different editions available for home, education, and enterprise users. It typically has a lower initial cost compared to Windows Server.
- Windows Server: Licensed on a per-core basis, with different editions offering varying levels of features and functionality. Its licensing model is more complex and often requires a higher initial investment.
2. User Interface and Functionality:
- Windows 10: Boasts a visually appealing and intuitive user interface designed for individual use. It includes features like the Start Menu, Taskbar, and Action Center, facilitating easy navigation and task management.
- Windows Server: Employs a server-centric interface, prioritizing administrative tasks and server management. It features a command-line interface, PowerShell, and administrative tools for managing users, network resources, and applications.
3. Features and Capabilities:
- Windows 10: Offers a wide array of features for personal and business use, including built-in applications like Microsoft Edge, OneDrive, and Windows Defender. It also supports a vast ecosystem of third-party applications.
- Windows Server: Provides specialized features designed for server management and hosting applications. It offers tools for Active Directory management, remote desktop services, virtualization, and network security.
4. Security and Stability:
- Windows 10: Features robust security measures, including Windows Defender, SmartScreen, and automatic updates, to protect against malware and unauthorized access. It prioritizes user experience and ease of use.
- Windows Server: Focuses on enterprise-grade security and stability, offering features like BitLocker encryption, Secure Boot, and advanced security auditing. It employs a stricter approach to security, prioritizing data protection and system integrity.
5. Scalability and Performance:
- Windows 10: Designed for individual and small business use, offering sufficient performance for everyday tasks. Its scalability is limited by the hardware limitations of the device.
- Windows Server: Built for scalability and performance, supporting large-scale deployments and demanding workloads. It can handle high traffic and data volumes, ensuring consistent performance even under heavy load.
6. Applications and Services:
- Windows 10: Supports a wide range of applications, including productivity suites, entertainment software, and gaming applications. It offers access to the Microsoft Store for downloading and installing applications.
- Windows Server: Focuses on hosting applications and providing services. It supports various server roles, including web server, file server, and database server, enabling businesses to deploy and manage their own applications.
7. Support and Maintenance:
- Windows 10: Receives regular updates and security patches. Microsoft provides support for various editions, with different levels of support available depending on the edition and licensing.
- Windows Server: Receives long-term support, with extended security updates and bug fixes. Microsoft offers dedicated support channels for Windows Server, providing assistance for complex issues and server management.
8. Virtualization:
- Windows 10: While Windows 10 supports virtualization, its capabilities are limited compared to Windows Server. It is primarily used for running virtual machines for development or testing purposes.
- Windows Server: Offers advanced virtualization features, allowing organizations to create and manage virtual machines on physical servers. It supports technologies like Hyper-V, enabling efficient resource utilization and server consolidation.
9. Cloud Integration:
- Windows 10: Integrates seamlessly with cloud services like OneDrive and Microsoft 365, providing cloud storage and collaboration features.
- Windows Server: Offers robust cloud integration capabilities, supporting Azure services and enabling hybrid cloud deployments. It allows organizations to extend their on-premises infrastructure to the cloud, enhancing scalability and flexibility.
Use Cases:
- Windows 10: Ideal for personal computers, laptops, tablets, and small businesses. It provides a user-friendly experience, robust security, and access to a vast application ecosystem.
- Windows Server: Suitable for large organizations, data centers, and businesses requiring robust server infrastructure. It provides a platform for managing networks, hosting applications, and storing data securely and reliably.
FAQs:
1. Can I use Windows Server for personal use?
While technically possible, it is not recommended. Windows Server is designed for enterprise environments and lacks the user-friendly features and applications found in Windows 10. Its licensing model is also more complex and expensive for personal use.
2. Can I run Windows 10 on a server?
While technically possible, it is not recommended. Windows 10 is not optimized for server environments and lacks the features and stability necessary for managing critical infrastructure. It is also not licensed for server use.
3. Which is better: Windows 10 or Windows Server?
The "better" option depends on the specific use case and requirements. Windows 10 excels in personal computing and small business environments, while Windows Server shines in enterprise-grade deployments and server management.
4. Can I upgrade from Windows 10 to Windows Server?
No, upgrading directly from Windows 10 to Windows Server is not possible. They are distinct operating systems with different functionalities and licensing models.
5. What is the difference between Windows Server and Windows Server Core?
Windows Server Core is a streamlined version of Windows Server, offering a minimal user interface and reduced footprint. It is ideal for server environments where a graphical interface is not required and resource efficiency is paramount.
Tips:
- For personal use: Choose Windows 10 for a user-friendly experience, robust security, and access to a wide range of applications.
- For small businesses: Consider Windows 10 for its ease of use and cost-effectiveness. However, if you require server-grade functionality, Windows Server may be a better option.
- For large organizations and data centers: Opt for Windows Server for its enterprise-grade features, scalability, and security.
Conclusion:
Windows 10 and Windows Server cater to distinct user needs and environments. Windows 10 is a user-friendly operating system designed for personal computing and small businesses, while Windows Server is a robust platform tailored for enterprise deployments and server management. Understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions about operating systems for your specific needs. Whether you are an individual user seeking a reliable and user-friendly experience or an organization demanding robust server infrastructure, the right choice between Windows 10 and Windows Server will ensure optimal performance and efficiency.



![Windows 10 vs Windows Server: [Differences Explained] WhatsaByte](https://whatsabyte.com/wp-content/uploads/windows-vs-windows-server.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into windows 10 versus windows server. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!