When Windows 10 Refuses To Boot: A Comprehensive Guide To Troubleshooting And Recovery
When Windows 10 Refuses to Boot: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Recovery
Related Articles: When Windows 10 Refuses to Boot: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Recovery
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to When Windows 10 Refuses to Boot: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Recovery. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
When Windows 10 Refuses to Boot: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Recovery

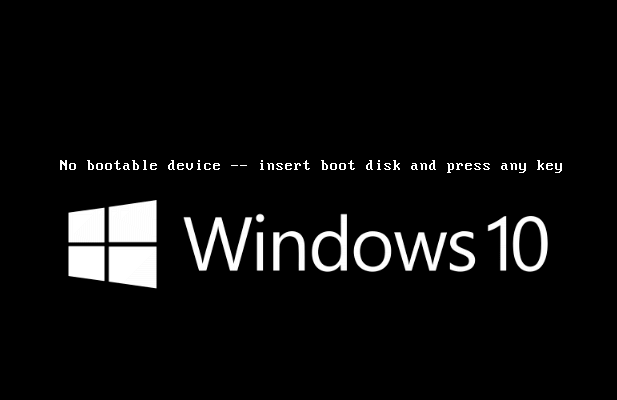
The dreaded "black screen of death" – a scenario familiar to many computer users – can be a frustrating experience. When Windows 10 fails to start, it can disrupt workflows, halt projects, and leave you stranded without access to your digital world. While the cause of this issue can vary greatly, understanding the potential culprits and the available troubleshooting steps can empower you to resolve the problem effectively.
Understanding the Problem
Before diving into solutions, it’s crucial to comprehend the underlying reasons for Windows 10’s inability to boot. The issue could stem from a wide range of factors, including:
- Hardware Malfunctions: Faulty components like the hard drive, RAM, or motherboard can prevent the system from starting.
- Software Conflicts: Corrupted system files, incompatible drivers, or malware infections can disrupt the boot process.
- Boot Configuration Errors: Incorrect boot settings, missing or damaged boot files, or improper partitioning can lead to a failed boot.
- Power Issues: Fluctuations in power supply or insufficient power can disrupt the boot sequence.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can damage components and lead to system instability, including boot failures.
Troubleshooting Steps: A Systematic Approach
Navigating the troubleshooting process requires a methodical approach. Start with the simplest solutions and work your way up, eliminating potential causes as you go.
1. Basic Checks:
- Power Cycle: A simple restart can sometimes resolve temporary glitches. Turn off your computer completely, unplug it for a few seconds, and then plug it back in and power it on.
- Check Connections: Ensure all cables, including the power cord, monitor cable, and any external peripherals, are securely connected.
- Remove External Devices: Disconnect all external devices, such as USB drives, printers, and external hard drives, to rule out any conflicts.
2. Boot Options:
- Safe Mode: Safe Mode starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services, helping to isolate problems caused by software conflicts or corrupted drivers. To access Safe Mode, restart your computer and repeatedly press the F8 key during the boot process.
- Last Known Good Configuration: This option reverts Windows to the last configuration that successfully booted. Access this option from the Advanced Boot Options menu by pressing F8 during startup.
- System Restore: System Restore allows you to roll back your system to a previous point in time, potentially undoing changes that caused the boot failure. Access System Restore from the Advanced Boot Options menu.
3. Advanced Troubleshooting:
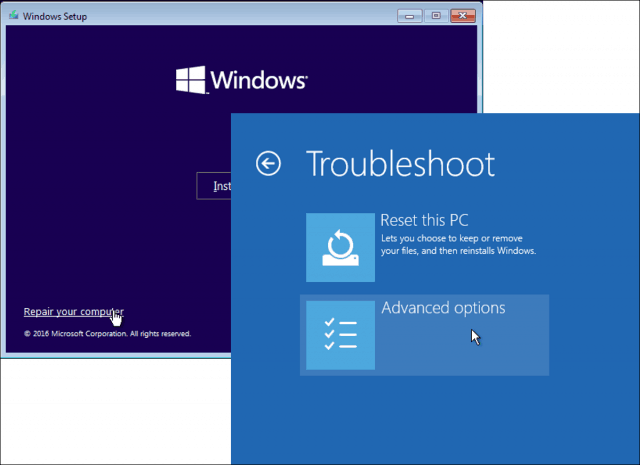
- Boot into the Recovery Environment: The Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) offers a suite of tools to diagnose and repair boot problems. Access WinRE by restarting your computer and repeatedly pressing the F8 key, then selecting "Repair your computer."
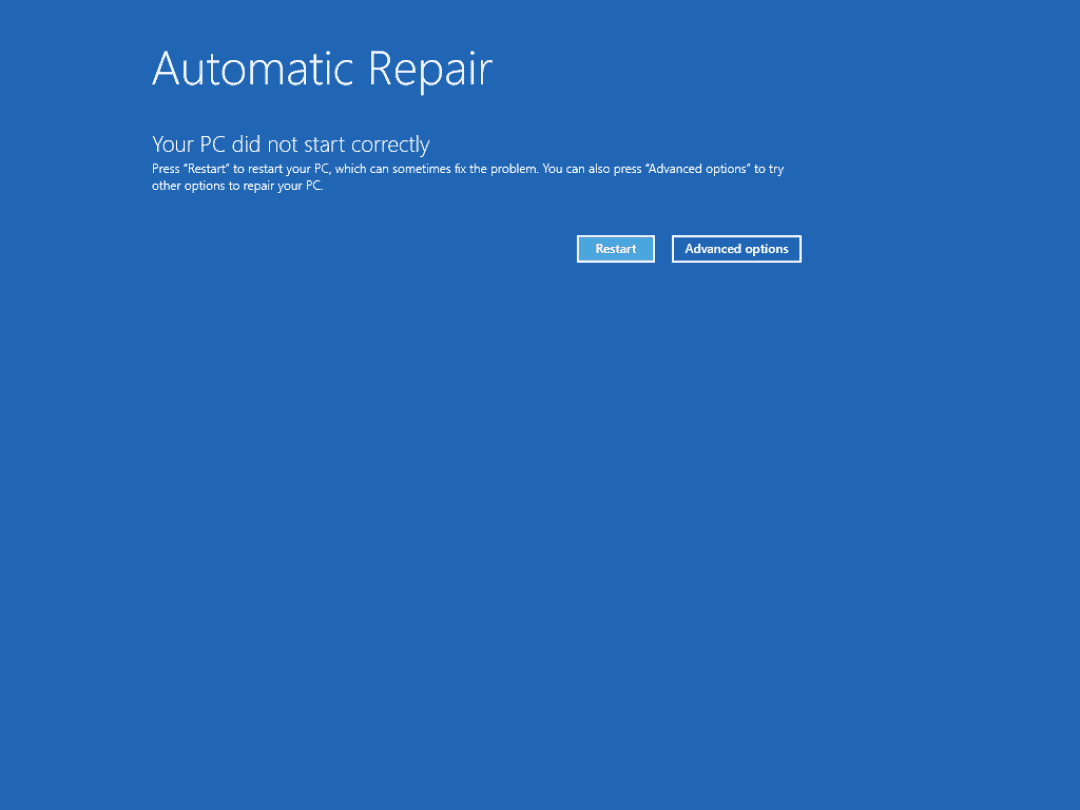
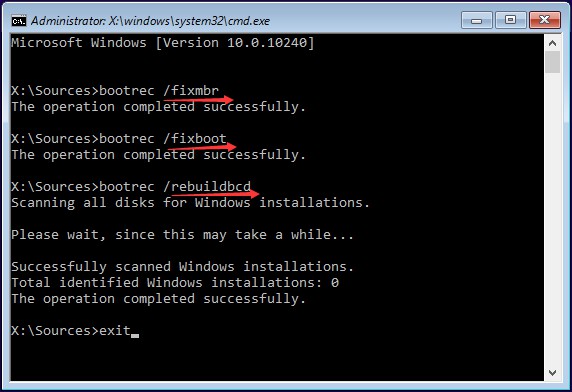
- Use the Startup Repair Tool: The Startup Repair tool automatically scans for and fixes problems that prevent Windows from starting correctly. Access it from the WinRE.
-
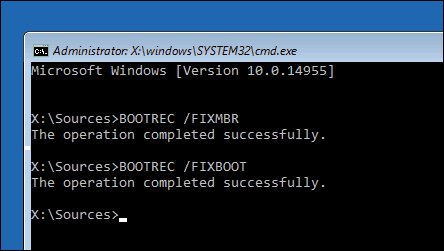
Run a System File Checker Scan: The System File Checker (SFC) tool scans for and repairs corrupted system files. Open Command Prompt from the WinRE and run the command
sfc /scannow. - Use a Bootable USB Drive: Create a bootable USB drive with a Windows 10 installation media. This allows you to access advanced repair options, including reinstalling Windows or repairing the boot files.
4. Hardware Considerations:
- Memory (RAM) Test: Run a memory test to identify any faulty RAM modules. Many motherboards have built-in memory test utilities accessible during the boot process.
- Hard Drive Check: Utilize the manufacturer’s diagnostic tools or third-party software to check the hard drive for errors.
- BIOS/UEFI Settings: Check the BIOS or UEFI settings for any incorrect configurations related to boot order or other settings.
5. Additional Steps:
- Check for Updates: Ensure that your system is running the latest Windows updates, as these often include bug fixes and security patches.
- Run Antivirus Scan: Scan your system for malware infections, which can disrupt the boot process.
- Contact Support: If all else fails, consider contacting Microsoft support for assistance or seeking help from a qualified technician.
FAQs
Q: My computer displays an error message during startup. How can I troubleshoot this?
A: Error messages provide valuable clues about the problem. Note the specific error message and search for it online. Many error codes have dedicated troubleshooting guides available.
Q: What if I cannot access the Advanced Boot Options menu?
A: If you cannot access the Advanced Boot Options menu, you can try using a bootable USB drive with a Windows 10 installation media. This allows you to access repair tools and potentially bypass the boot issue.
Q: What if I suspect a hardware failure?
A: If you suspect a hardware failure, you should contact a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair. Attempting to diagnose or repair hardware issues yourself can be risky and potentially damage your computer further.
Tips
- Regularly Back Up Your Data: Create regular backups of your important files and system settings. This will ensure that you can recover your data even if you need to reinstall Windows.
- Keep Your System Updated: Install the latest Windows updates and driver updates to ensure stability and security.
- Monitor System Health: Use system monitoring tools to track your computer’s temperature and resource usage. Overheating can lead to boot issues.
- Be Cautious with Software Downloads: Download software only from trusted sources to minimize the risk of malware infections.
Conclusion
Encountering a "black screen of death" can be a frustrating experience, but it is not insurmountable. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined above, you can systematically diagnose and address the underlying causes of Windows 10 boot failures. Remember to be patient, methodical, and consult reputable resources when needed. With a bit of perseverance, you can restore your computer to a functional state and regain access to your digital life.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into When Windows 10 Refuses to Boot: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Recovery. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!