Unraveling The Mystery Of Windows 10’s "Fast Startup"
Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10’s "Fast Startup"
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10’s "Fast Startup"
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10’s "Fast Startup". Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10’s "Fast Startup"
In the realm of operating systems, speed and efficiency are paramount. Windows 10, Microsoft’s latest iteration, boasts a feature designed to dramatically reduce boot times, making the user experience smoother and more responsive. This feature, often referred to as "Fast Startup," is not a simple shortcut but a complex mechanism that leverages a hybrid approach to system startup.
Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Startup
Traditional computer startup involves a series of steps, beginning with the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), followed by loading the operating system from the hard drive, and finally, initializing applications and services. This process can be time-consuming, especially on older machines or those with large amounts of data.
Fast Startup, however, introduces a clever twist. Instead of performing a full shutdown, it enters a "hybrid shutdown" state. During this state, the operating system kernel and device drivers are stored in a hibernation file on the hard drive. This file effectively acts as a snapshot of the system’s core components, allowing for a much faster restart.
Upon initiating a "Fast Startup," Windows 10 does not go through the entire boot sequence. Instead, it bypasses the BIOS and directly loads the kernel and drivers from the hibernation file. This significantly reduces the time required to start the system, resulting in a noticeably quicker user experience.
Benefits of Fast Startup
The benefits of Fast Startup are undeniable:
-
Reduced Boot Times: This is the most noticeable advantage. Users can expect to see a significant decrease in the time it takes for their computer to become fully operational.
-
Improved Responsiveness: The faster boot times translate into a more responsive system overall, as applications and services launch quicker and the user interface feels snappier.
-
Enhanced User Experience: The overall user experience is enhanced by the seamless transition between shutdown and restart, making the entire process feel more intuitive and efficient.
Potential Drawbacks
While Fast Startup offers numerous advantages, it is not without its potential drawbacks:
-
Slower Shutdowns: The process of saving the kernel and drivers to the hibernation file can add a few seconds to the shutdown process.
-
Increased Disk Usage: The hibernation file can take up a significant amount of disk space, potentially impacting storage availability, especially on systems with limited hard drive capacity.
-
Compatibility Issues: Certain hardware or software configurations might not be fully compatible with Fast Startup, potentially leading to unexpected behavior or errors.
FAQs on Fast Startup
Q: Is Fast Startup the same as hibernation?
A: While both Fast Startup and hibernation involve saving the system state, they operate differently. Hibernation saves the entire system’s memory to the hard drive, while Fast Startup only saves the kernel and drivers. Fast Startup is generally faster, but it doesn’t save the entire system state like hibernation.
Q: Is Fast Startup always enabled?
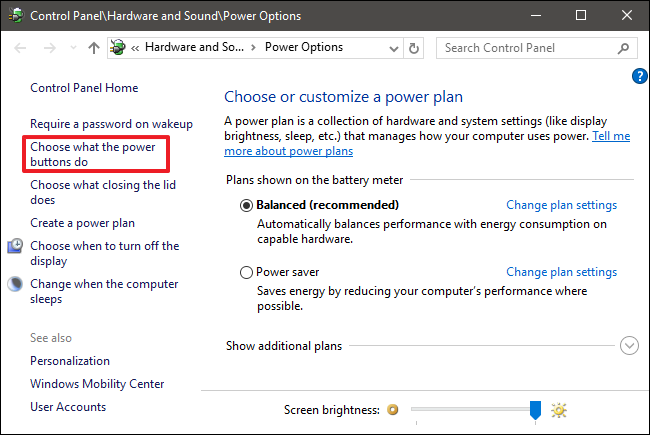
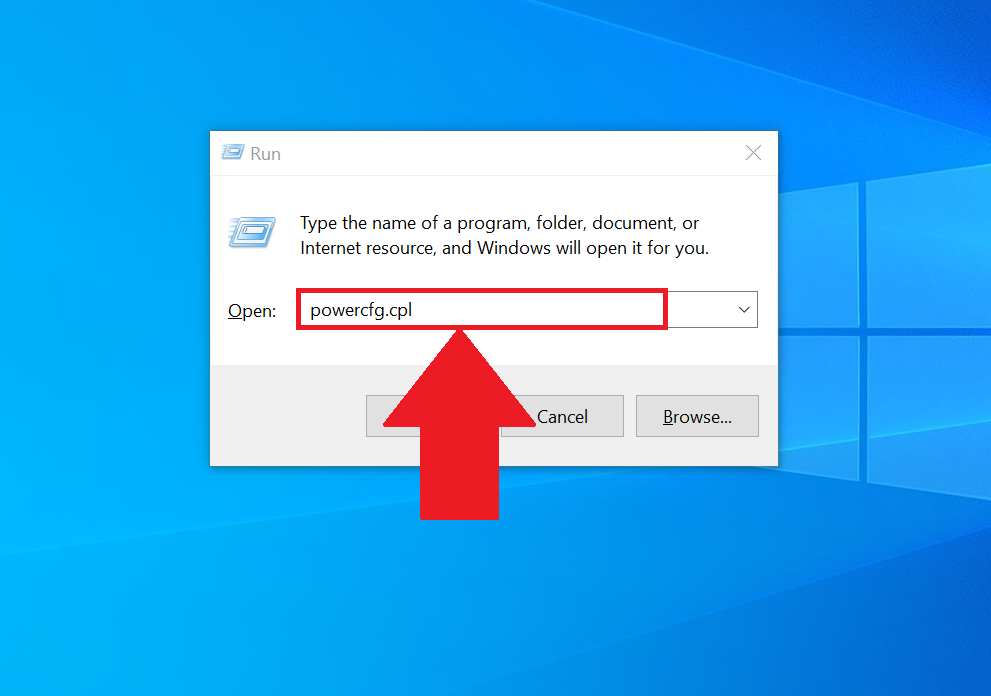
A: Fast Startup is enabled by default in Windows 10, but users can disable it if needed. This can be done through the Power Options settings in the Control Panel.
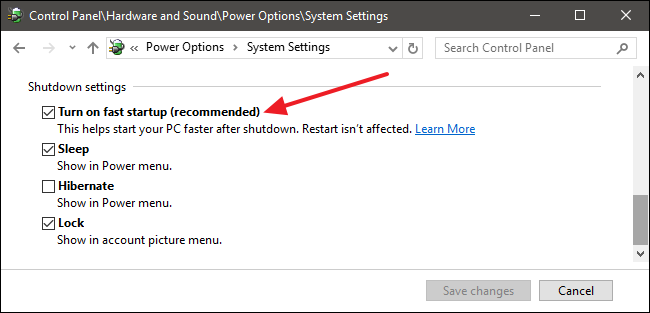
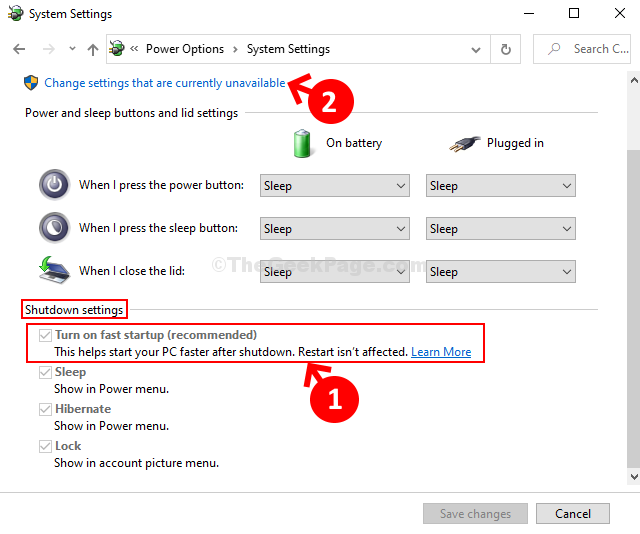
Q: How do I know if Fast Startup is enabled?
A: You can check the status of Fast Startup by navigating to the Power Options settings in the Control Panel. Look for the "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" option. If it is checked, Fast Startup is enabled.
Q: Does Fast Startup affect battery life?
A: While Fast Startup generally doesn’t have a significant impact on battery life, it can consume more power during the shutdown process due to saving the kernel and drivers.
Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup
-
Ensure Sufficient Disk Space: Make sure your hard drive has enough free space to accommodate the hibernation file.
-
Update Drivers: Keep your system’s drivers up-to-date to ensure compatibility with Fast Startup.
-
Disable Unnecessary Programs: Minimize the number of programs that start automatically when Windows boots to reduce boot times.
-
Defragment Hard Drive: Regularly defragmenting your hard drive can improve performance and potentially enhance Fast Startup efficiency.
Conclusion
Fast Startup is a valuable feature in Windows 10 that significantly enhances the user experience by reducing boot times and improving system responsiveness. While it has some potential drawbacks, its benefits outweigh the downsides for most users. Understanding the mechanics and potential issues associated with Fast Startup allows users to make informed decisions about its use and optimize its performance for a smoother and more efficient computing experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10’s "Fast Startup". We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!