Unraveling The Mystery Of Disabled Hibernate In Windows 10
Unraveling the Mystery of Disabled Hibernate in Windows 10
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery of Disabled Hibernate in Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mystery of Disabled Hibernate in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Mystery of Disabled Hibernate in Windows 10

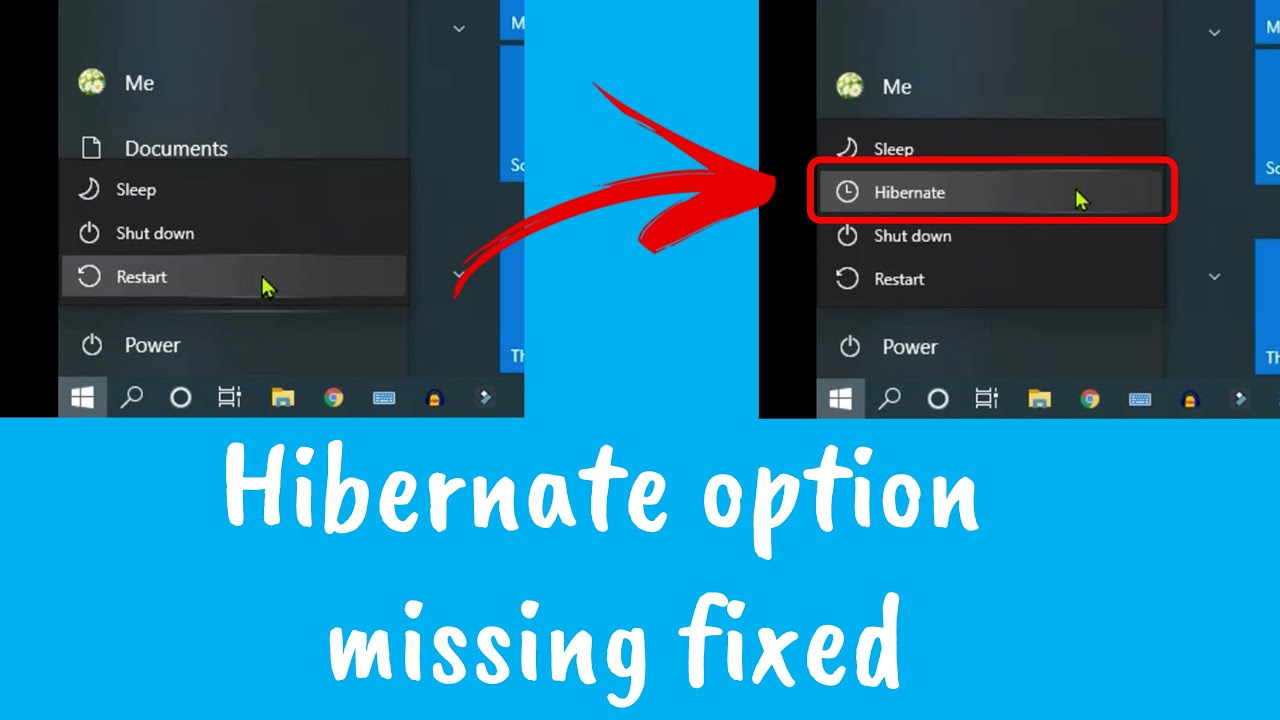
Windows 10, despite its robust feature set, occasionally presents users with perplexing scenarios. One such enigma is the disappearance of the hibernate option, leaving users wondering about its absence and potential implications. This article delves into the complexities behind this phenomenon, providing a comprehensive understanding of the reasons behind a disabled hibernate mode and offering practical solutions to restore its functionality.
Understanding Hibernate: A Power Management Tool
Hibernate, a power management feature intrinsic to Windows operating systems, offers a unique approach to system shutdown. Unlike sleep mode, which maintains a low-power state, hibernate saves the system’s current state to the hard drive and completely shuts down the computer. This allows for a swift and seamless resumption of operations upon restarting, as the system reverts to the exact state it was in before entering hibernate mode.
Why is Hibernate Disabled? A Multifaceted Issue
The absence of the hibernate option in Windows 10 can stem from various factors, each demanding a distinct approach for resolution. These factors can range from simple configuration errors to more intricate system issues.
1. Insufficient Disk Space:
Hibernate requires adequate disk space to store the system’s memory contents. If the hard drive lacks sufficient free space, Windows disables hibernate to prevent potential data corruption or system instability.
2. Hardware Compatibility Issues:
Certain hardware configurations, particularly those involving older or less compatible components, may not fully support hibernate. This incompatibility can lead to system malfunctions during the hibernation process, prompting Windows to disable the feature as a safety measure.
3. System File Corruption:
Corruption within critical system files can disrupt the hibernation process, causing errors or unexpected behavior. Windows, in an attempt to safeguard system integrity, may disable hibernate to prevent further complications.
4. Power Plan Settings:
Windows power plans, which govern the system’s energy consumption behavior, can influence the availability of hibernate. Some power plans may have hibernate disabled by default, requiring manual adjustments.
5. Group Policy Restrictions:
System administrators, particularly in corporate or educational environments, may enforce group policies restricting access to specific features, including hibernate. These restrictions aim to enhance security or maintain system stability.
6. Third-Party Software Interference:
Occasionally, third-party software, particularly those managing system resources or power settings, can interfere with the hibernation process. This interference may lead to unexpected behavior or instability, prompting Windows to disable hibernate.
7. Windows Update Issues:
Certain Windows updates, while intended to improve system performance and security, can inadvertently cause conflicts with the hibernation functionality. These conflicts can lead to errors or unpredictable behavior, forcing Windows to disable hibernate.
Resolving the Hibernate Dilemma: A Practical Guide
Addressing the absence of hibernate requires a systematic approach, focusing on identifying the underlying cause and implementing appropriate solutions.
1. Check Disk Space:
Ensure sufficient free space on the hard drive, ideally at least the size of the system’s RAM. If disk space is limited, consider deleting unnecessary files or upgrading storage capacity.
2. Verify Hardware Compatibility:
Ensure compatibility of all hardware components, particularly the hard drive and RAM, with hibernate functionality. Consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek support from the hardware vendor.
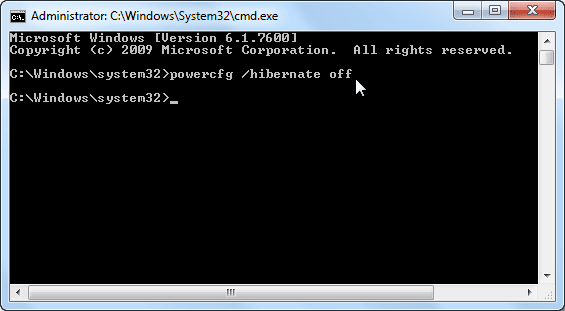
3. Run System File Checker:
Utilize the System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan for and repair corrupted system files. This can be accessed through the Command Prompt (cmd) by typing "sfc /scannow" and pressing Enter.
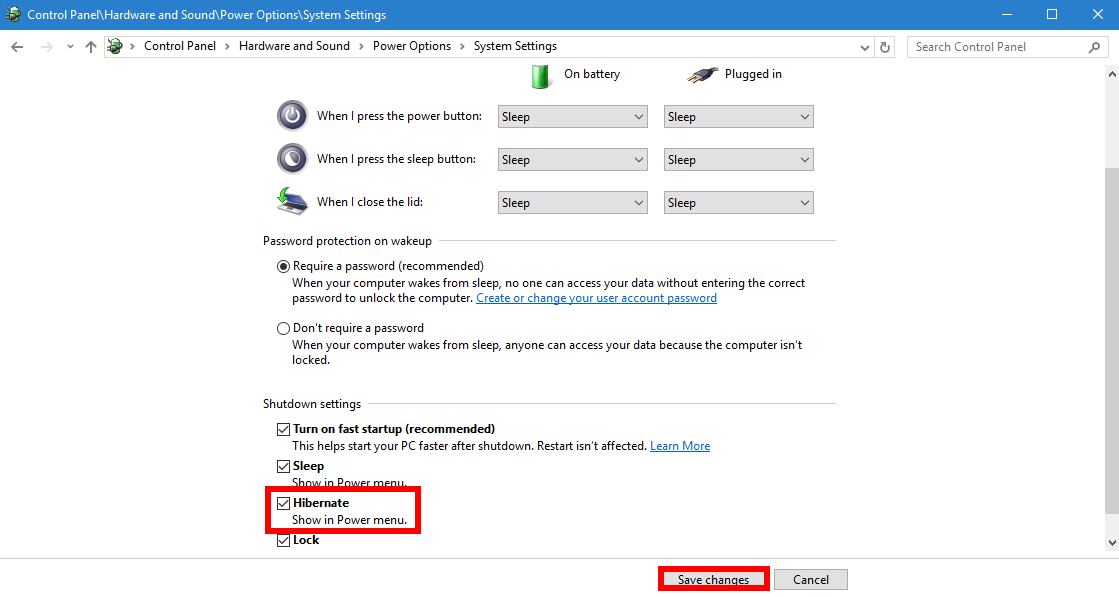
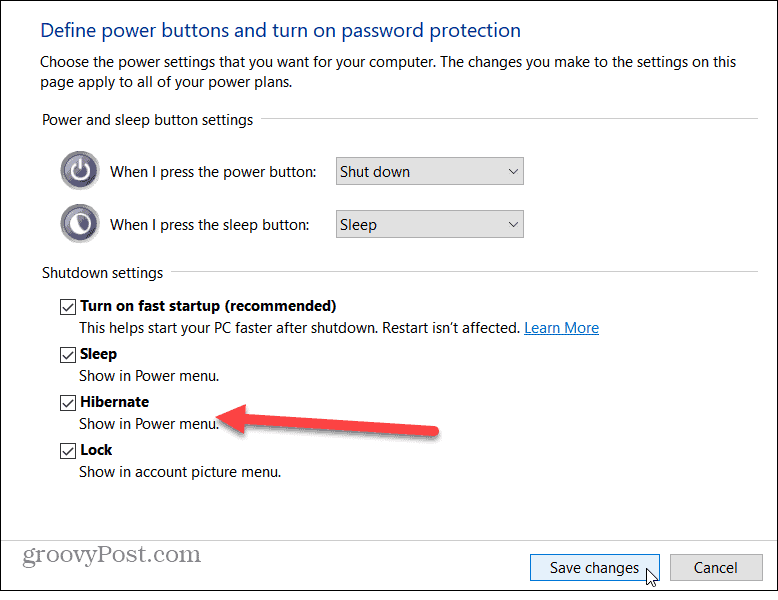
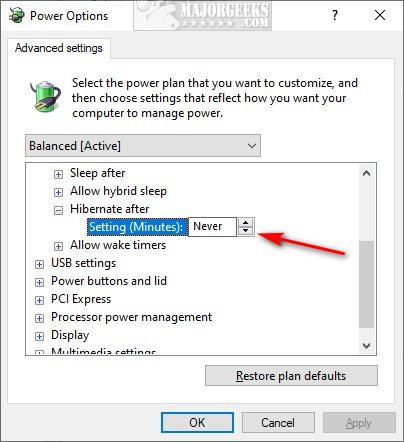
4. Adjust Power Plan Settings:
Access the power plan settings by searching for "Power Options" in the Windows search bar. Select the desired power plan and click on "Change plan settings." Within the advanced power settings, locate "Hibernate" and ensure it is enabled.
5. Review Group Policies:
If operating within a managed environment, contact the system administrator to inquire about potential group policy restrictions affecting hibernate.
6. Disable Third-Party Software:
Temporarily disable any third-party software that might interfere with hibernate. Observe system behavior after disabling the software to determine if it resolves the issue.
7. Reinstall Windows Updates:
If recent Windows updates coincide with the disappearance of hibernate, consider reinstalling or rolling back the updates. This can be done through the Windows Update settings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is it normal for hibernate to be disabled in Windows 10?
While not inherently normal, it is not uncommon for hibernate to be disabled due to various factors. The absence of hibernate does not necessarily indicate a system malfunction.
2. Can I enable hibernate without sufficient disk space?
No, enabling hibernate without adequate disk space can lead to system instability or data corruption. Ensure sufficient free space before attempting to enable hibernation.
3. Is there a way to force hibernate even if it’s disabled?
There are no readily available methods to force hibernate if it’s disabled by Windows. Addressing the underlying cause is crucial for restoring hibernate functionality.
4. What are the benefits of using hibernate?
Hibernate offers several benefits, including:
- Fast system resumption: Resuming from hibernate is significantly faster than booting from a cold shutdown.
- Power savings: Hibernate consumes minimal power, reducing energy consumption compared to sleep mode.
- Data preservation: All open applications and documents are saved, allowing for seamless resumption of work.
5. Can I use hibernate if I have a Solid State Drive (SSD)?
Yes, SSDs generally support hibernation, offering even faster resume times compared to traditional hard drives.
Tips for Optimizing Hibernate Functionality
- Regularly clean up disk space: Delete unnecessary files and programs to maintain sufficient free space for hibernate.
- Keep system files up to date: Regularly update Windows and drivers to ensure compatibility and prevent potential conflicts.
- Monitor system behavior: Observe system performance during hibernation and identify any potential issues.
- Consider using a power plan that supports hibernate: Select a power plan that prioritizes energy efficiency and enables hibernate functionality.
Conclusion
The absence of hibernate in Windows 10 can be a frustrating experience, but understanding the underlying causes and employing appropriate solutions can effectively address the issue. By systematically addressing potential factors, users can restore hibernate functionality and enjoy its benefits for efficient system management and power savings.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mystery of Disabled Hibernate in Windows 10. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!