Understanding CPU Temperature In Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of your computer, responsible for executing all the instructions that make your system function. Like any complex piece of machinery, the CPU generates heat during operation. This heat, if not adequately managed, can lead to performance degradation, instability, and even hardware damage. Monitoring CPU temperature is crucial for ensuring optimal system health and longevity.
The Importance of CPU Temperature Monitoring
Sustained high CPU temperatures can have detrimental effects on your system:
- Performance Degradation: High temperatures can cause the CPU to throttle its performance to prevent overheating, leading to sluggish operation and reduced responsiveness.
- System Instability: Excessive heat can lead to crashes, freezes, and other system errors, disrupting your workflow.
- Hardware Damage: If the CPU temperature reaches critical levels, it can permanently damage the processor, requiring costly repairs or replacement.
- Reduced Lifespan: Sustained high temperatures can shorten the lifespan of your CPU, necessitating an earlier replacement.
Windows 10 Tools for Monitoring CPU Temperature
Fortunately, Windows 10 offers several built-in tools and third-party applications that allow you to monitor CPU temperature, ensuring you can identify and address any potential issues before they escalate.
1. Task Manager
The Task Manager is a versatile tool that provides real-time system information, including CPU temperature. To access it, right-click on the taskbar and select "Task Manager" or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Performance Tab: This tab provides a graphical representation of CPU usage, memory usage, and disk activity. While it doesn’t directly display the CPU temperature, it can be used to identify periods of high CPU utilization, which often coincide with increased heat generation.
- Resource Monitor: Click on the "More details" button in Task Manager to access the Resource Monitor, a more detailed view of system resources. Navigate to the "CPU" tab, and you’ll find the "Temperature" section, which displays the current CPU temperature.
2. Event Viewer
The Event Viewer logs system events, including warnings and errors. If your CPU temperature is reaching critical levels, the Event Viewer may record error messages related to overheating. To access the Event Viewer, search for "Event Viewer" in the Windows search bar. Navigate to "Windows Logs" > "System" to view system-related events.
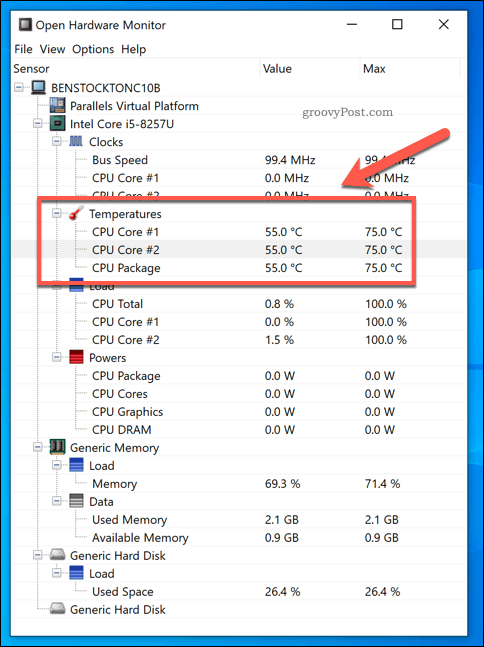
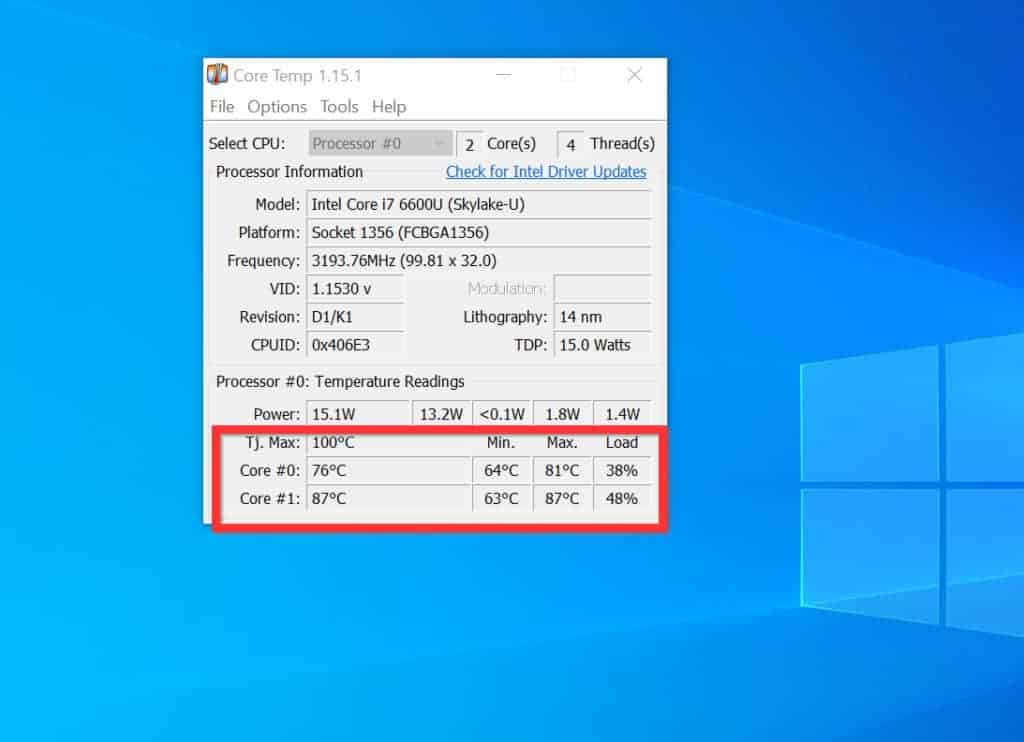
3. Third-Party Monitoring Software
Many third-party monitoring software programs offer comprehensive system monitoring capabilities, including detailed CPU temperature readings. Some popular options include:
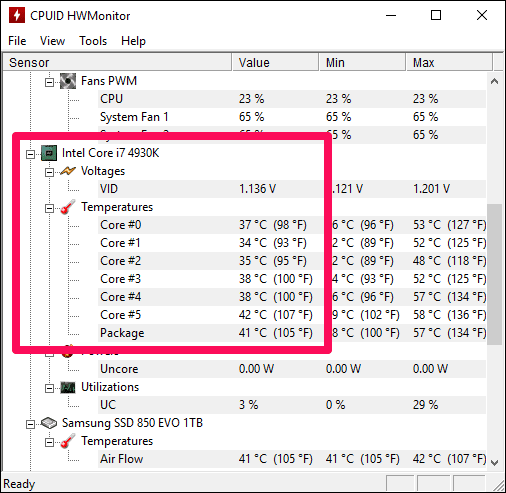
- HWMonitor: A free and open-source tool that provides detailed information about your system’s hardware, including CPU temperature, fan speeds, and voltage readings.
- CPU-Z: A popular utility that provides information about your CPU, including its temperature, clock speed, and other specifications.
- MSI Afterburner: A popular overclocking tool that also includes real-time system monitoring features, including CPU temperature.
Interpreting CPU Temperature Readings
CPU temperature readings vary depending on the CPU model, workload, and ambient temperature. However, a general guideline is:
- Idle Temperature: A typical idle CPU temperature should range between 30°C to 45°C (86°F to 113°F).
- Load Temperature: Under heavy workloads, such as gaming or video editing, CPU temperatures can reach 70°C to 90°C (158°F to 194°F).
- Critical Temperature: Different CPUs have varying critical temperature thresholds, but exceeding 100°C (212°F) can pose a serious risk of hardware damage.
Troubleshooting High CPU Temperatures
If you’re experiencing high CPU temperatures, here are some troubleshooting steps:
- Ensure Proper Cooling: Ensure your CPU cooler is properly installed and functioning correctly. Clean dust and debris from the cooler and heatsink.
- Check Fan Speeds: Verify that your CPU fan is spinning at an appropriate speed. If it’s not, you may need to replace the fan.
- Monitor Background Processes: Identify and close any unnecessary programs running in the background that could be consuming excessive CPU resources.
- Optimize System Settings: Adjust power settings to favor performance over energy saving, and consider disabling unnecessary background services.
- Consider Re-applying Thermal Paste: Over time, the thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink can dry out, reducing its effectiveness. Re-applying fresh thermal paste can improve heat dissipation.
- Increase Ambient Airflow: Ensure adequate airflow around your computer to help dissipate heat. Consider using a cooling pad or improving ventilation in your workspace.
FAQs about CPU Temperature in Windows 10
1. What is the normal CPU temperature for Windows 10?
The normal CPU temperature varies depending on the CPU model, workload, and ambient temperature. Generally, idle temperatures between 30°C to 45°C (86°F to 113°F) are considered normal, while load temperatures can reach 70°C to 90°C (158°F to 194°F).
2. How do I check my CPU temperature in Windows 10?
You can check your CPU temperature using the Task Manager (Resource Monitor), Event Viewer, or third-party monitoring software like HWMonitor or CPU-Z.
3. Is it bad if my CPU is hot?
Sustained high CPU temperatures can lead to performance degradation, system instability, and even hardware damage. It’s important to monitor CPU temperature and take steps to address any issues before they escalate.
4. What should I do if my CPU temperature is too high?
If your CPU temperature is too high, you should first ensure proper cooling, check fan speeds, monitor background processes, and optimize system settings. If these steps don’t resolve the issue, you may need to consider re-applying thermal paste or increasing ambient airflow.
5. How can I prevent my CPU from overheating?
To prevent CPU overheating, ensure proper cooling, monitor background processes, optimize system settings, and avoid running demanding applications for extended periods without adequate ventilation.
Tips for Managing CPU Temperature in Windows 10
- Regularly Clean Your System: Dust and debris can accumulate on your CPU cooler and heatsink, hindering heat dissipation. Regularly clean your system to ensure proper airflow.
- Use a Cooling Pad: A cooling pad can help improve airflow around your laptop or desktop computer, reducing CPU temperature.
- Monitor Background Processes: Identify and close any unnecessary programs running in the background that could be consuming excessive CPU resources.
- Optimize Power Settings: Adjust power settings to favor performance over energy saving, particularly when running demanding applications.
- Avoid Overclocking: Overclocking your CPU can increase performance but also generates more heat. If you’re not experienced with overclocking, it’s best to avoid it.
Conclusion
Monitoring CPU temperature is an essential part of maintaining the health and performance of your Windows 10 system. By understanding the factors that contribute to CPU temperature, utilizing available monitoring tools, and taking proactive steps to address potential issues, you can ensure your system operates efficiently and reliably for years to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!