Understanding And Resolving High CPU Usage In Windows 11
Understanding and Resolving High CPU Usage in Windows 11
Related Articles: Understanding and Resolving High CPU Usage in Windows 11
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Resolving High CPU Usage in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Resolving High CPU Usage in Windows 11
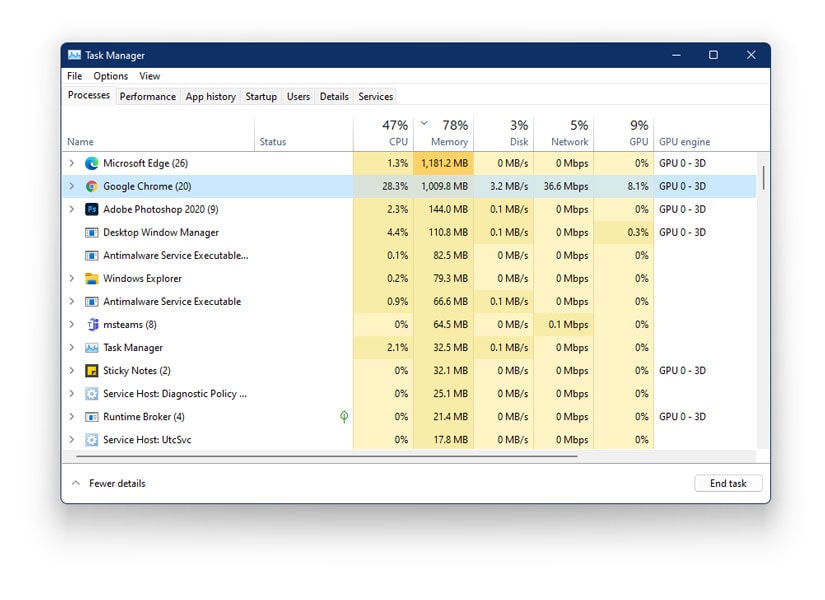
High CPU utilization, often manifested as a 100% CPU load, is a common issue that can significantly impact the performance of a Windows 11 computer. It can lead to sluggish responsiveness, application crashes, and overall system instability. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the causes of high CPU usage in Windows 11, offering solutions and troubleshooting techniques to restore optimal performance.
Understanding CPU Utilization
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of a computer, responsible for executing instructions and processing data. CPU utilization refers to the percentage of time the CPU is actively working. A 100% CPU load indicates that the CPU is fully engaged in processing tasks, leaving no room for other operations.
Causes of High CPU Usage in Windows 11
High CPU usage can be attributed to a variety of factors, ranging from resource-intensive applications to background processes consuming excessive system resources. Here are some common culprits:
1. Resource-Intensive Applications:
- Gaming: Modern games often demand significant processing power, potentially leading to high CPU utilization.
- Video Editing and Rendering: Software like Adobe Premiere Pro and After Effects utilize substantial CPU resources during video editing and rendering tasks.
- 3D Modeling and Animation: Applications such as Blender and Maya require considerable CPU power for complex 3D modeling and animation processes.
- Streaming: Streaming services like Netflix and YouTube utilize CPU resources for video decoding and playback.
2. Background Processes:
- Antivirus Software: Real-time antivirus scans can consume significant CPU resources, particularly during initial scans or when encountering suspicious files.
- System Updates: Windows Update downloads and installs updates in the background, potentially leading to temporary CPU spikes.
- Cloud Synchronization: Services like OneDrive and Dropbox continuously synchronize files, utilizing CPU resources for data transfer and processing.
- Malware and Viruses: Malicious software can consume CPU resources for various nefarious purposes, such as data theft or cryptocurrency mining.
3. Hardware Issues:
- Overheating: Overheating can cause CPU throttling, leading to reduced performance and potentially high CPU utilization as the processor tries to compensate for the heat.
- Faulty Hardware: Damaged or malfunctioning hardware components, such as RAM or the motherboard, can contribute to system instability and high CPU usage.
4. Software Conflicts:
- Driver Issues: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can cause conflicts and lead to high CPU usage.
- Software Bugs: Bugs within applications or operating system components can trigger CPU-intensive processes, resulting in high utilization.
5. System Configuration:
- Overclocking: Overclocking the CPU can increase performance but also increase heat generation and potentially lead to instability.
- Excessive Startup Programs: A large number of programs running at startup can consume significant CPU resources, leading to slow performance and high CPU usage.
Diagnosing High CPU Usage
Identifying the root cause of high CPU usage is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Here are some methods to diagnose the issue:
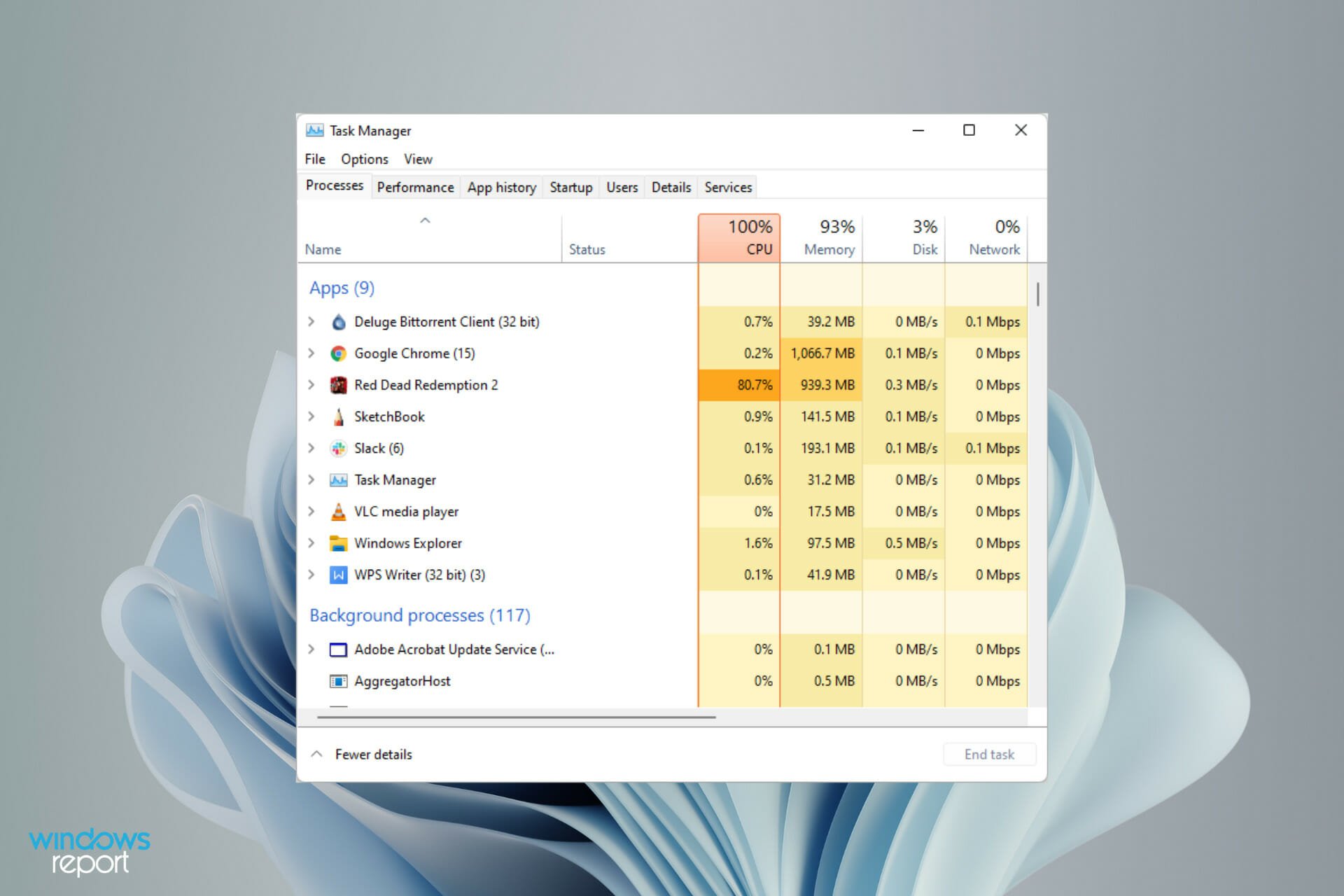
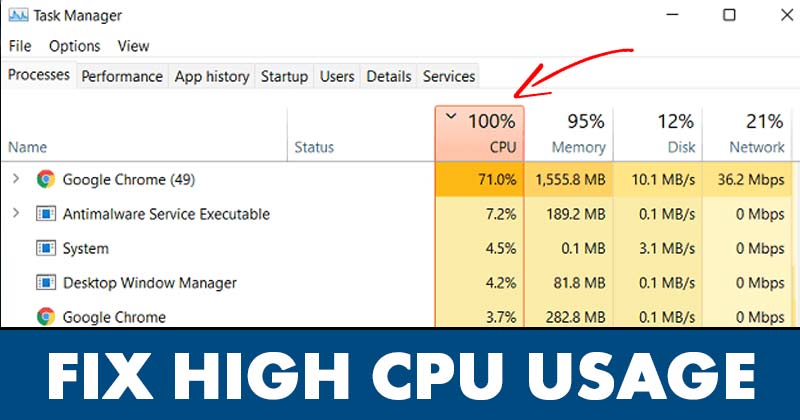
1. Task Manager:
- Open Task Manager: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- View Processes: Switch to the Processes tab.
- Sort by CPU: Sort the processes by CPU usage to identify the most resource-intensive programs.
- Analyze Processes: Examine the processes consuming high CPU resources and determine their purpose.
- End Task: If a specific application is causing the high CPU usage, right-click on it and select End task.
2. Resource Monitor:
- Open Resource Monitor: Search for "Resource Monitor" in the Windows search bar.
- CPU Tab: Navigate to the CPU tab.
- Process Activity: Analyze the CPU activity of different processes over time.
- Identify Culprits: Focus on processes with consistently high CPU utilization and investigate their nature.
3. Event Viewer:
- Open Event Viewer: Search for "Event Viewer" in the Windows search bar.
- Windows Logs: Navigate to Windows Logs > System.
- Filter Events: Filter events by the Error or Warning severity levels.
- Investigate Errors: Analyze error messages related to CPU activity or system performance.
4. System Information:
- Open System Information: Search for "System Information" in the Windows search bar.
- Hardware Resources: Explore the Hardware Resources section.
- Identify Components: Review the information about hardware components, including the CPU, RAM, and storage devices.
- Check for Errors: Look for any error messages or warnings related to hardware components.
Troubleshooting High CPU Usage
Once the cause of high CPU usage has been identified, you can implement the following troubleshooting techniques:
1. Close Resource-Intensive Applications:
- Identify and Terminate: Identify the resource-intensive applications using Task Manager and terminate them.
- Prioritize Essential Processes: Close applications that are not currently in use to free up CPU resources for essential tasks.
2. Manage Background Processes:
- Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs: Use the Startup tab in Task Manager to disable programs that launch automatically at startup.
- Review Scheduled Tasks: Check the Task Scheduler for any unnecessary scheduled tasks that consume CPU resources.
- Optimize System Services: Use the Services console to disable or delay startup of non-essential system services.
3. Update Drivers:
- Check for Updates: Visit the manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest drivers for your hardware components.
- Use Device Manager: Use the Device Manager to update drivers for specific devices.
4. Scan for Malware:
- Run a Full Scan: Use a reliable antivirus program to perform a full system scan for malware.
- Update Antivirus Definitions: Ensure your antivirus software has the latest virus definitions to detect and remove the latest threats.
5. Check for Overheating:
- Monitor Temperatures: Use monitoring software to check the temperature of your CPU and other components.
- Improve Cooling: Ensure adequate airflow by cleaning dust from the computer’s interior and using a cooling pad.
6. Repair System Files:
- Run System File Checker (SFC): Use the command sfc /scannow in Command Prompt to scan and repair corrupted system files.
- Run Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM): Use the command DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth in Command Prompt to repair system images.
7. Perform a Clean Boot:
- Start in Safe Mode: Restart the computer and press F8 during startup to access the boot options and select Safe Mode.
- Disable Startup Programs: Disable startup programs in the System Configuration window.
- Identify the Culprit: Observe the CPU usage in Safe Mode to determine if the issue is caused by a specific startup program.
8. Reset Windows 11:
- Reset to Factory Settings: Use the Reset this PC option in Windows settings to restore the system to its factory defaults.
- Preserve Personal Files: Choose the option to preserve personal files during the reset process to avoid data loss.
FAQs
Q: What is the ideal CPU utilization for Windows 11?
A: While there is no universal ideal, a CPU utilization below 80% is generally considered optimal. However, the acceptable range can vary depending on the workload and system specifications.
Q: How do I know if high CPU usage is a problem?
A: High CPU usage becomes a problem when it significantly impacts system performance, leading to slow responsiveness, application crashes, or overall system instability.
Q: What are the potential consequences of ignoring high CPU usage?
A: Ignoring high CPU usage can lead to system instability, application crashes, data loss, and even hardware damage due to overheating.
Tips
- Monitor CPU Usage Regularly: Use Task Manager or other monitoring tools to track CPU utilization and identify any unusual spikes.
- Prioritize Essential Tasks: Close unnecessary applications and background processes to free up CPU resources for critical tasks.
- Optimize System Settings: Adjust power settings, disable unnecessary startup programs, and optimize system services to minimize CPU usage.
- Keep System Updated: Install the latest Windows updates and device drivers to ensure optimal system performance.
- Run Regular Scans: Use antivirus software to scan for malware and keep your system protected from threats.
Conclusion
High CPU usage in Windows 11 can be a frustrating issue, but understanding the causes and implementing the appropriate troubleshooting techniques can restore optimal system performance. By closely monitoring CPU utilization, identifying the root cause, and taking proactive steps to manage background processes and optimize system settings, you can ensure a smooth and efficient Windows 11 experience. Remember that a well-maintained system with optimized settings and regular maintenance can significantly reduce the chances of encountering high CPU usage issues.





![How To Fix High CPU Usage in Windows 11[Solved] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/syZVC3poeno/hqdefault.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Resolving High CPU Usage in Windows 11. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!