Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: When Safe Mode Fails
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: When Safe Mode Fails
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: When Safe Mode Fails
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: When Safe Mode Fails. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: When Safe Mode Fails
Windows 10, while generally robust, can encounter situations where it fails to boot normally. In such scenarios, booting into Safe Mode becomes a crucial troubleshooting tool. Safe Mode is a diagnostic environment that loads Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services, effectively isolating potential issues. However, situations arise where even accessing Safe Mode proves challenging. This article delves into the complexities of this scenario, exploring the underlying causes, offering comprehensive troubleshooting steps, and outlining potential solutions.
Understanding Safe Mode and its Significance
Safe Mode is a vital tool for Windows users facing boot issues. It provides a stripped-down environment, allowing users to:
- Identify and resolve driver conflicts: Faulty or incompatible drivers are frequent culprits behind boot problems. Safe Mode, by loading only essential drivers, can help pinpoint the problematic driver.
- Troubleshoot malware infections: Some malware can prevent Windows from booting properly. Safe Mode, with its limited services, can be used to run antivirus scans and remove malicious software.
- Repair corrupted system files: System file corruption can lead to boot failures. Safe Mode allows access to system repair tools, enabling users to restore or repair damaged files.
- Test hardware components: By loading a minimal set of drivers, Safe Mode can help isolate hardware malfunctions that may be causing boot problems.
Common Causes of Safe Mode Failure
The inability to access Safe Mode can stem from various factors:
- Corrupted Boot Files: Essential boot files, such as boot.ini or BCD (Boot Configuration Data), can become corrupted, hindering the loading of Safe Mode.
- Driver Issues: A faulty driver, particularly a graphics or network driver, can interfere with Safe Mode’s loading process.
- Malware Interference: Malicious software can actively block access to Safe Mode, preventing users from accessing the diagnostic environment.
- Hardware Failures: A failing hard drive, RAM issues, or a malfunctioning motherboard can all contribute to Safe Mode inaccessibility.
- Incorrect Boot Settings: Misconfigured boot settings, such as improper boot order or disabled boot options, can prevent Safe Mode from launching.
Troubleshooting Steps: A Comprehensive Guide
Addressing Safe Mode failure requires a systematic approach. Here’s a detailed breakdown of troubleshooting steps:
1. Restarting the Computer:
- Begin by restarting your computer. This simple step can resolve minor glitches and temporary issues that might be preventing Safe Mode from loading.
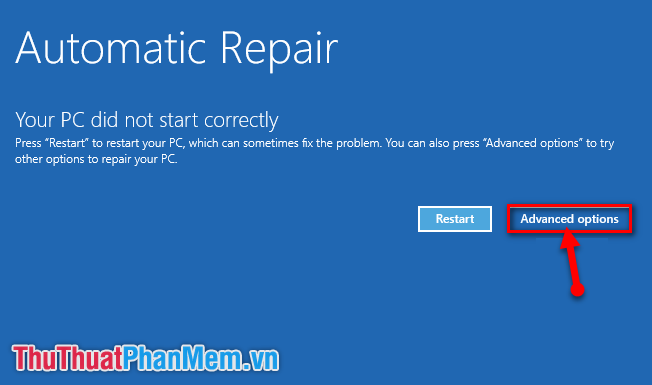
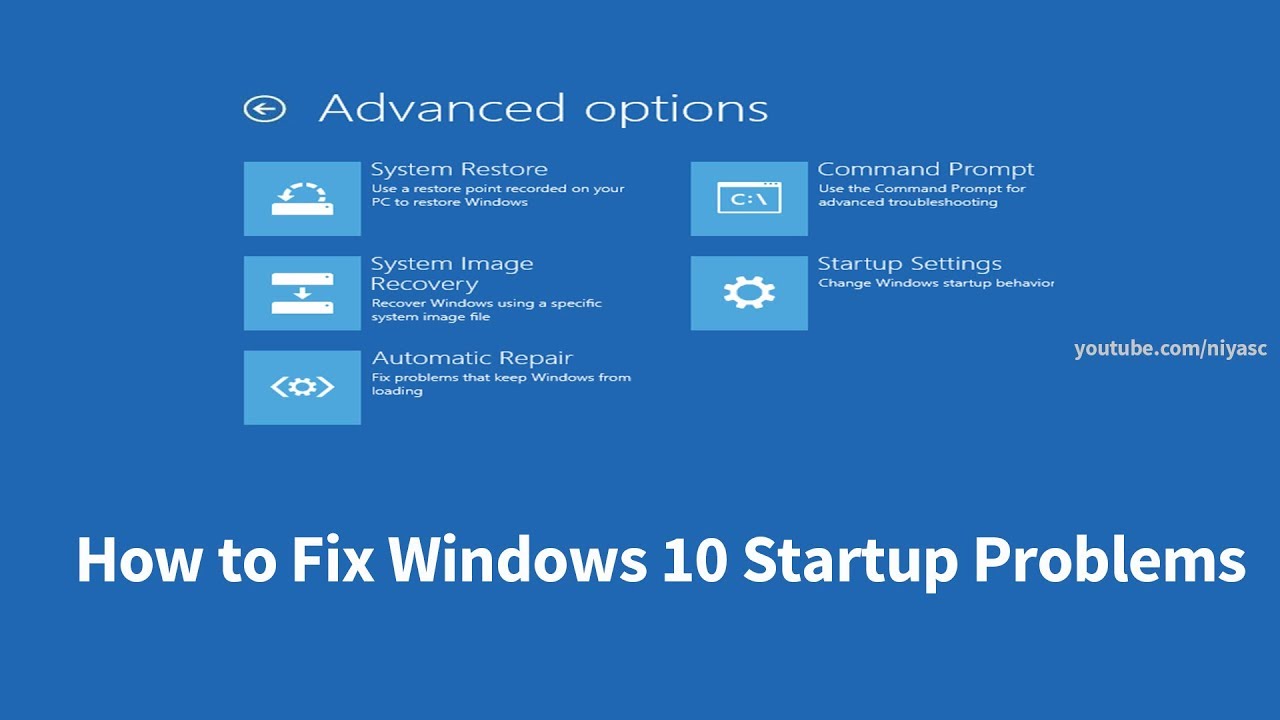
2. Accessing the Advanced Startup Options:
- If restarting doesn’t resolve the issue, access the Advanced Startup Options menu. This menu offers various tools for troubleshooting boot problems.
-
Windows 10:
- Press and hold the Shift key while clicking the "Restart" option in the Start menu.
- Alternatively, open the Settings app, navigate to "Update & Security," and select "Recovery." Click "Restart now" under "Advanced Startup."
-
Windows 11:
- Open the Settings app, navigate to "System," and select "Recovery." Click "Restart now" under "Advanced Startup."
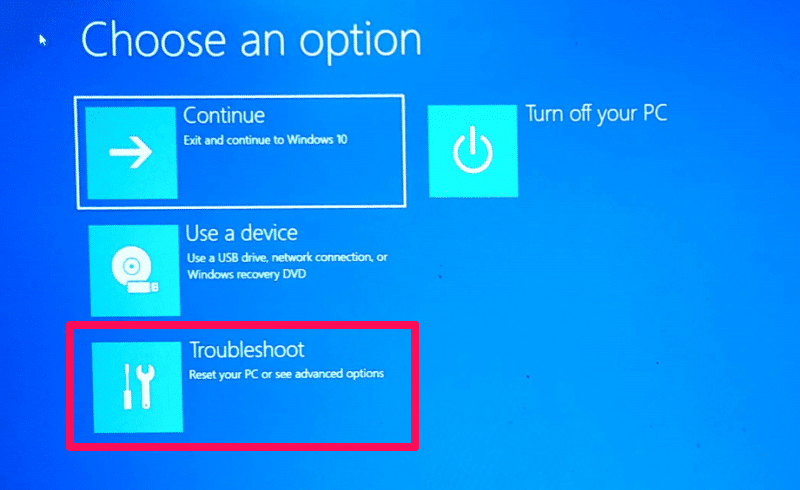
3. Attempting Safe Mode from the Advanced Startup Options:
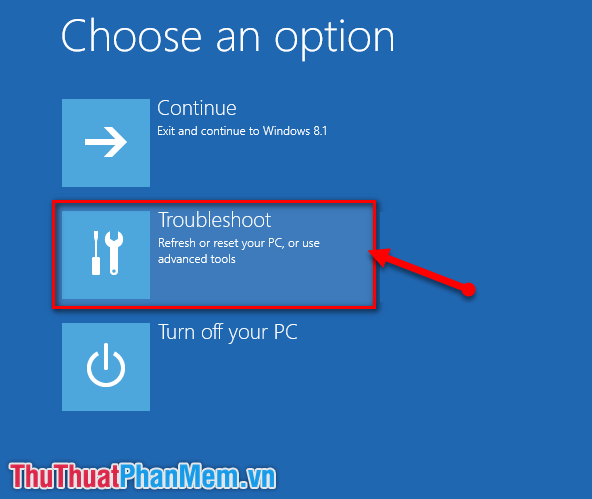
- Once in the Advanced Startup Options menu, choose "Troubleshoot."
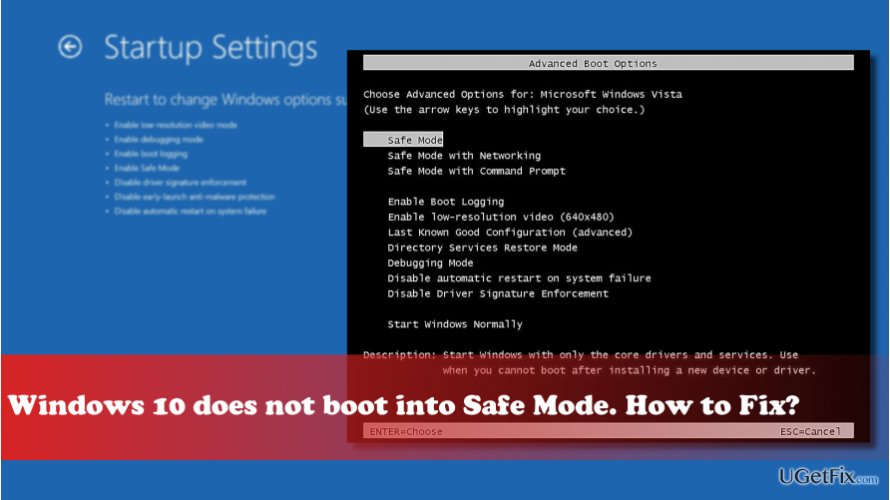
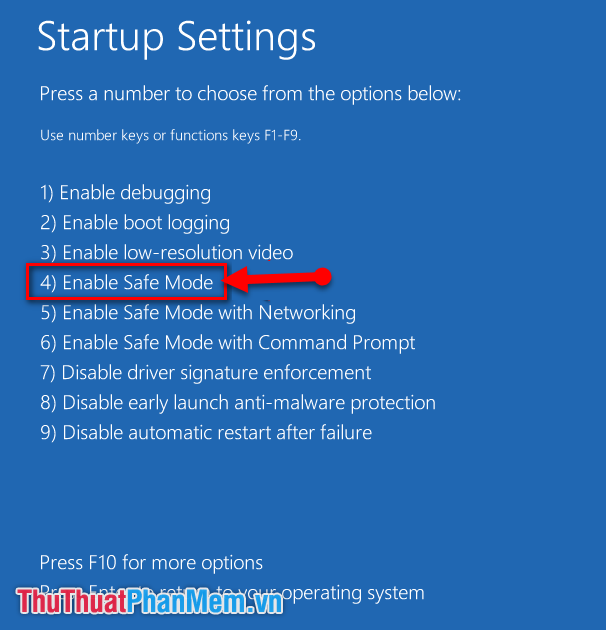
- Select "Advanced options" and then "Startup Settings."
- Click "Restart" and then press the corresponding number key (usually 4 or F4) to enter Safe Mode.
- If Safe Mode still fails to load, proceed to the next steps.
4. Using the System Configuration Utility (msconfig):
- Access the System Configuration utility (msconfig) by searching for it in the Start menu.
- Navigate to the "Boot" tab and ensure that "Safe boot" is checked.
- Select the desired Safe Mode option (minimal, network, or command prompt) and apply the changes.
- Restart your computer. This will attempt to load Windows in Safe Mode.
- If Safe Mode still fails to load, proceed to the next steps.
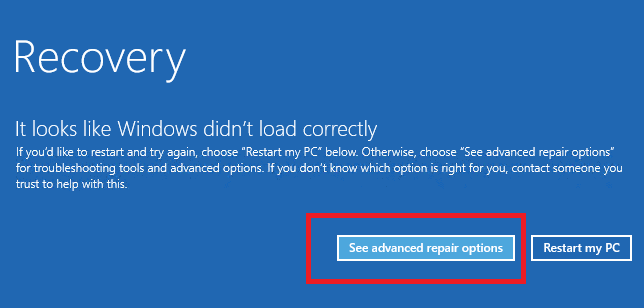
5. Running Startup Repair:
- In the Advanced Startup Options menu, choose "Troubleshoot" and then "Advanced options."
- Select "Startup Repair." This tool scans and attempts to fix boot-related issues.
- Allow the repair process to complete. Restart your computer after the process is finished.
- If Startup Repair doesn’t resolve the issue, proceed to the next steps.
6. Using a System Restore Point:
- If a system restore point is available, it can be used to revert your computer to a previous state, potentially resolving the Safe Mode issue.
- In the Advanced Startup Options menu, choose "Troubleshoot" and then "Advanced options."
- Select "System Restore." Follow the on-screen instructions to choose a restore point and restore your system.
- Restart your computer after the restore process is complete.
- If System Restore doesn’t resolve the issue, proceed to the next steps.
7. Performing a Clean Boot:
- A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services, similar to Safe Mode. This helps identify potential conflicts.
- Access the System Configuration utility (msconfig).
- On the "General" tab, select "Selective startup" and uncheck "Load startup items."
- Navigate to the "Services" tab and check "Hide all Microsoft services."
- Click "Disable all" to disable all non-Microsoft services.
- Click "Apply" and "OK."
- Restart your computer.
- If Safe Mode now loads, you can gradually enable services and drivers to identify the culprit.
- If Safe Mode still fails to load, proceed to the next steps.
8. Reinstalling Windows:
- If all other troubleshooting steps fail, reinstalling Windows might be necessary. This will completely erase your hard drive and install a fresh copy of Windows.
- Before reinstalling Windows, ensure you have a backup of your important data.
- Use a bootable USB drive or DVD containing the Windows installation media.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Can I access Safe Mode without using the Advanced Startup Options menu?
A: While accessing Safe Mode directly from the Windows login screen is possible in older versions of Windows, this method is often unreliable in Windows 10. It’s generally recommended to use the Advanced Startup Options menu for a more stable approach.
Q: Can I use Safe Mode to remove a virus or malware?
A: Yes, Safe Mode can be used to run antivirus scans and remove malware, especially if the infection prevents Windows from booting normally. However, it’s crucial to use a reputable antivirus program and follow its instructions carefully.
Q: What if Safe Mode loads but the issue persists?
A: If Safe Mode loads but the original problem persists, it indicates that the issue is not related to drivers or services. The problem might be hardware-related or require further troubleshooting steps specific to the issue.
Q: Can I use Safe Mode to recover lost data?
A: While Safe Mode doesn’t directly offer data recovery tools, it can be used to access data recovery software or to copy data to another drive if the original drive is malfunctioning.
Tips: Enhancing Troubleshooting Success
- Keep a record of your troubleshooting steps: Documenting your actions can help you retrace your steps and identify potential errors.
- Consider using a bootable USB drive: Creating a bootable USB drive with a live operating system like Linux can provide a safe environment to access your hard drive and troubleshoot issues.
- Consult online resources: Numerous forums, websites, and communities dedicated to Windows troubleshooting can offer valuable insights and solutions.
- Seek professional help: If you are unable to resolve the issue independently, consider seeking help from a qualified technician.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Smooth Windows Experience
The inability to access Safe Mode can be a frustrating experience, but it’s important to remember that it’s often a symptom of a larger issue. By systematically troubleshooting the problem using the steps outlined in this article, users can pinpoint the root cause and implement the appropriate solutions. Understanding the underlying causes and employing a comprehensive approach can significantly improve the chances of restoring Windows to a functional state.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: When Safe Mode Fails. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!