The Role Of KMS Servers In Windows 10 And 11 Licensing
The Role of KMS Servers in Windows 10 and 11 Licensing
Related Articles: The Role of KMS Servers in Windows 10 and 11 Licensing
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Role of KMS Servers in Windows 10 and 11 Licensing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Role of KMS Servers in Windows 10 and 11 Licensing

The deployment and management of large-scale Windows environments within organizations necessitate efficient licensing strategies. One such approach, particularly relevant for businesses with multiple computers, is the utilization of Key Management Service (KMS) servers. This article explores the intricacies of KMS servers, focusing on their significance in facilitating Windows 10 and 11 licensing.
Understanding KMS Servers
KMS servers are a crucial component of Microsoft’s Volume Licensing program, designed to streamline the activation process for Windows operating systems and other Microsoft products within a network environment. Unlike traditional product keys, which are unique to each individual machine, KMS servers operate by granting temporary activation licenses to clients.
How KMS Servers Work
- Activation Request: When a Windows client attempts to activate, it first contacts the KMS server.
- License Verification: The KMS server checks if the client has a valid KMS license. This license is typically obtained through a Volume Licensing agreement with Microsoft.
- Activation Grant: If the client has a valid KMS license, the KMS server grants a temporary activation license for a specific duration.
- Renewal: Clients periodically reconnect with the KMS server to renew their activation licenses. This ensures continued functionality and prevents the need for individual product key management.
Benefits of Using KMS Servers
- Simplified Activation: KMS servers eliminate the need to manually activate each computer individually with unique product keys. This streamlines the process, especially in large-scale deployments.
- Centralized Management: KMS servers provide a centralized point of control for managing activation licenses. This simplifies administration and allows for easier monitoring of activation status across the network.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating the need for individual product keys, KMS servers can reduce the overall cost of licensing for large organizations.
- Enhanced Security: KMS servers help to protect against unauthorized activation attempts by enforcing licensing policies and verifying client identities.
KMS Server Requirements
To set up a KMS server, certain technical requirements must be met:
- Operating System: The KMS server must be running a supported version of Windows Server.
- Hardware: The server should have sufficient processing power, memory, and storage to handle the workload.
- Network Connectivity: The KMS server needs to be accessible to client computers on the network.
- KMS License: A valid KMS license key is required to activate the KMS server.
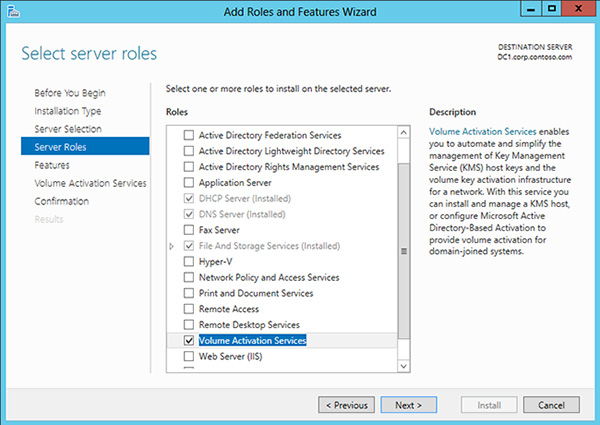
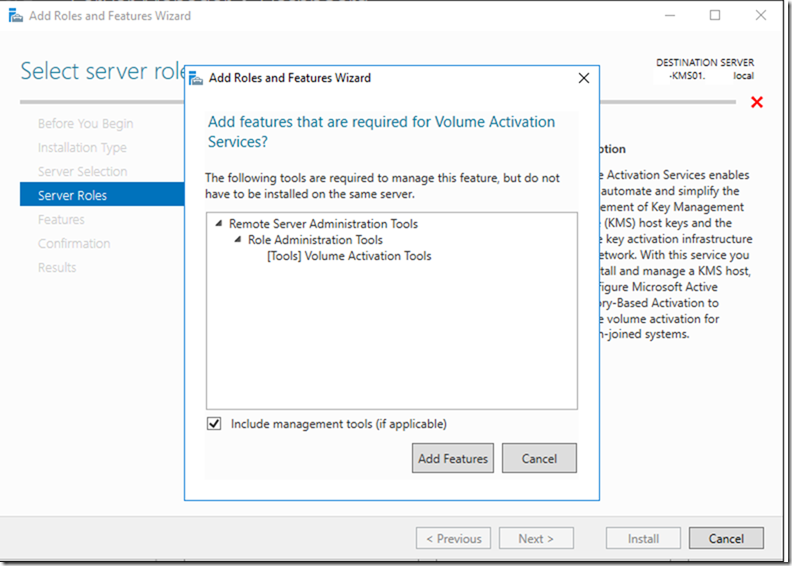
Creating a KMS Server
The process of setting up a KMS server involves the following steps:
- Install Windows Server: Install a supported version of Windows Server on the designated hardware.
-
Configure KMS Server: Utilize the
slmgr.vbscommand-line utility to configure the KMS server and install the KMS license key. -
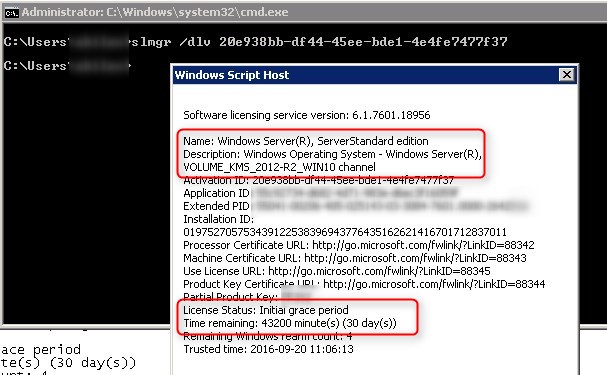
Activate KMS Server: Activate the KMS server using the
slmgr.vbscommand. - Client Configuration: Configure client computers to connect to the KMS server for activation.
KMS Server Activation for Windows 10/11
For Windows 10 and 11, the KMS activation process is similar to previous versions. Clients need to be configured to connect to the KMS server and obtain a temporary activation license. The activation process can be initiated through the Windows Settings app or by using the slmgr.vbs command.
FAQs about KMS Servers
Q: Can I use a KMS server for both Windows 10 and Windows 11 clients?
A: Yes, a single KMS server can typically be used for both Windows 10 and Windows 11 clients. However, ensure that the KMS server is configured with the appropriate KMS license for both operating systems.
Q: How often do clients need to renew their activation licenses with the KMS server?
A: Clients typically need to renew their activation licenses every 180 days. This can be done automatically by the system or manually through the slmgr.vbs command.
Q: What happens if the KMS server is unavailable?
A: If the KMS server is unavailable, clients will continue to function normally for a grace period. However, they will eventually require manual activation or access to a different KMS server.
Q: Can I use a KMS server for other Microsoft products besides Windows?
A: Yes, KMS servers can be used to activate other Microsoft products, including Office, SQL Server, and Exchange Server. However, separate KMS licenses are required for each product.
Tips for Using KMS Servers
- Plan Your Deployment: Before deploying a KMS server, carefully plan the network infrastructure and ensure that the server has sufficient resources.
- Secure Your KMS Server: Implement appropriate security measures to protect the KMS server from unauthorized access.
- Monitor Activation Status: Regularly monitor the activation status of client computers to ensure that they are properly licensed.
- Consider a KMS Host: For large organizations, consider using a dedicated KMS host server to improve performance and reliability.
Conclusion
KMS servers offer a powerful and efficient solution for managing Windows 10 and 11 licensing in large-scale deployments. By simplifying activation, centralizing management, and reducing costs, KMS servers enable organizations to effectively manage their licensing needs and ensure compliance with Microsoft’s licensing agreements. Proper understanding and implementation of KMS servers are crucial for maximizing the benefits of this licensing approach.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Role of KMS Servers in Windows 10 and 11 Licensing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!