The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements
The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements
Related Articles: The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements
- 3.1 The Core of Performance: Decoding CPU Requirements
- 3.2 The Importance of a Suitable CPU: Why it Matters
- 3.3 Matching the CPU to Your Needs: A Practical Guide
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Choosing the Right CPU
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Foundation of Performance
- 4 Closure
The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements
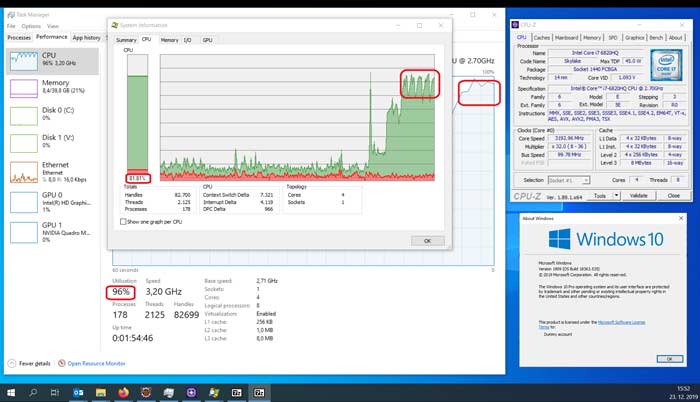
Windows 10, a widely adopted operating system, demands a certain level of processing power to function smoothly. This processing power is provided by the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the brain of your computer. The CPU’s capabilities directly impact the overall performance of your system, influencing how quickly applications launch, games run, and tasks are completed.
Understanding the CPU requirements for Windows 10 is essential for ensuring a seamless user experience. This article delves into the intricacies of these requirements, exploring their significance and providing insights into how to choose the right CPU for your needs.
The Core of Performance: Decoding CPU Requirements
Windows 10’s minimum CPU requirement is a 1 gigahertz (GHz) processor with support for PAE, NX, and SSE2 instructions. However, this minimum specification is only suitable for basic computing tasks, such as browsing the internet or using simple office applications. For a more robust and enjoyable experience, a more powerful CPU is recommended.
The CPU’s performance is measured in several key factors:
- Cores and Threads: Modern CPUs feature multiple cores, each capable of executing instructions independently. Multi-core processors allow for parallel processing, enabling faster execution of demanding tasks. Additionally, each core can have multiple threads, further enhancing parallel processing capabilities.
- Clock Speed: Measured in GHz, the clock speed determines how fast the CPU can execute instructions. Higher clock speeds generally translate to faster performance.
- Cache Size: The CPU cache acts as a temporary storage area for frequently accessed data. Larger cache sizes can lead to faster access times, improving overall performance.
- Instruction Set Architecture: This refers to the set of instructions the CPU understands and can execute. Advanced instruction sets, like SSE2, offer enhanced performance for specific tasks.
These factors combined determine the CPU’s overall processing power. A higher core count, faster clock speed, larger cache size, and advanced instruction set architecture result in a more powerful CPU.
The Importance of a Suitable CPU: Why it Matters
A CPU that meets or exceeds Windows 10’s minimum requirements ensures:
- Smooth and Responsive Operation: A powerful CPU ensures applications launch quickly, programs run smoothly, and the system responds promptly to user input.
- Enhanced Multitasking: With multiple cores and threads, the CPU can handle multiple tasks simultaneously without significant performance degradation. This is crucial for users who multitask frequently, running several applications simultaneously.
- Improved Gaming Performance: Modern games often demand significant processing power. A powerful CPU ensures smoother gameplay, higher frame rates, and a more immersive experience.
- Future-Proofing: Choosing a CPU with ample processing power ensures your system remains relevant for years to come, as software and applications become increasingly demanding.
Matching the CPU to Your Needs: A Practical Guide
Selecting the right CPU involves considering your specific needs and usage patterns. Here’s a breakdown of CPU recommendations based on different usage scenarios:
Basic Computing: For basic tasks like web browsing, email, and light office work, a dual-core CPU with a clock speed of 2.5 GHz or higher is sufficient.
Casual Gaming and Multimedia: For casual gaming and multimedia tasks like video editing, a quad-core CPU with a clock speed of 3.0 GHz or higher is recommended.
Heavy Gaming and Content Creation: For demanding tasks like high-end gaming, video editing, and 3D modeling, a six-core or eight-core CPU with a clock speed of 3.5 GHz or higher is essential.
Professional Applications: For professional applications requiring high processing power, such as scientific simulations or data analysis, consider CPUs with even more cores and threads, exceeding 10 cores in some cases.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: Can I upgrade my CPU after purchasing a computer?
A: Upgrading the CPU is typically not possible on pre-built systems. However, some motherboards offer socket compatibility for future CPU upgrades.
Q: What is the difference between a CPU and a GPU?
A: The CPU is responsible for general-purpose processing, while the GPU specializes in graphics processing. While both are crucial for a smooth user experience, the GPU plays a more prominent role in tasks like gaming and video editing.
Q: How can I check my current CPU’s specifications?
A: You can access your CPU information through the Windows Task Manager. Open the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc), navigate to the "Performance" tab, and select "CPU" to view details like the CPU model, core count, and clock speed.
Q: Can I use a CPU from a different manufacturer?
A: CPUs are designed for specific sockets, which are the connectors on the motherboard. You need to ensure that the CPU you choose is compatible with your motherboard’s socket.
Tips for Choosing the Right CPU
- Research and Compare: Thoroughly research different CPU models and compare their specifications, benchmarks, and user reviews.
- Consider Your Budget: CPUs vary significantly in price. Determine your budget and choose a CPU that provides the best value for your needs.
- Check for Compatibility: Ensure the CPU you choose is compatible with your motherboard’s socket and other system components.
- Look for Energy Efficiency: Modern CPUs offer varying levels of energy efficiency. Consider choosing a CPU with a lower TDP (Thermal Design Power) for better power consumption.
Conclusion: The Foundation of Performance
The CPU is the heart of your computer, driving its overall performance. Understanding Windows 10’s CPU requirements is crucial for ensuring a smooth, responsive, and enjoyable user experience. By carefully considering your needs and choosing a CPU that meets or exceeds the recommended specifications, you can unlock the full potential of your system and enjoy a seamless computing experience. Remember, a well-chosen CPU is an investment in a robust and future-proof computing platform.




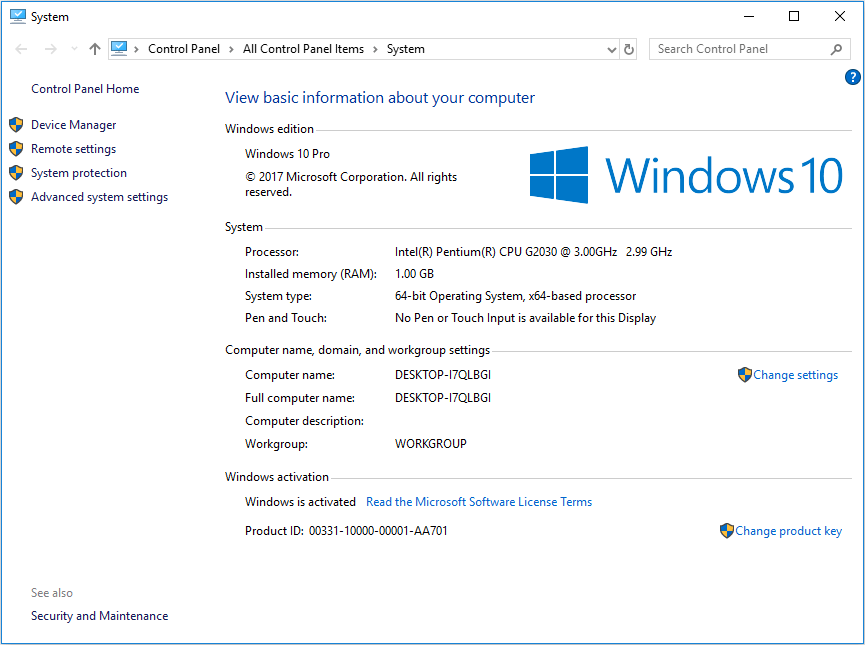
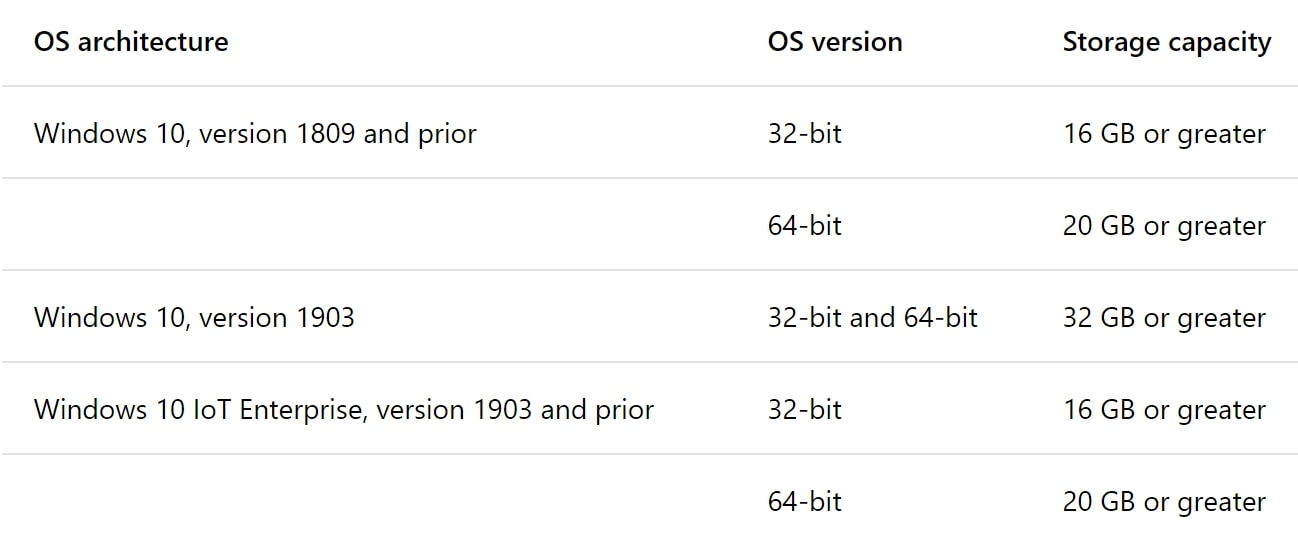
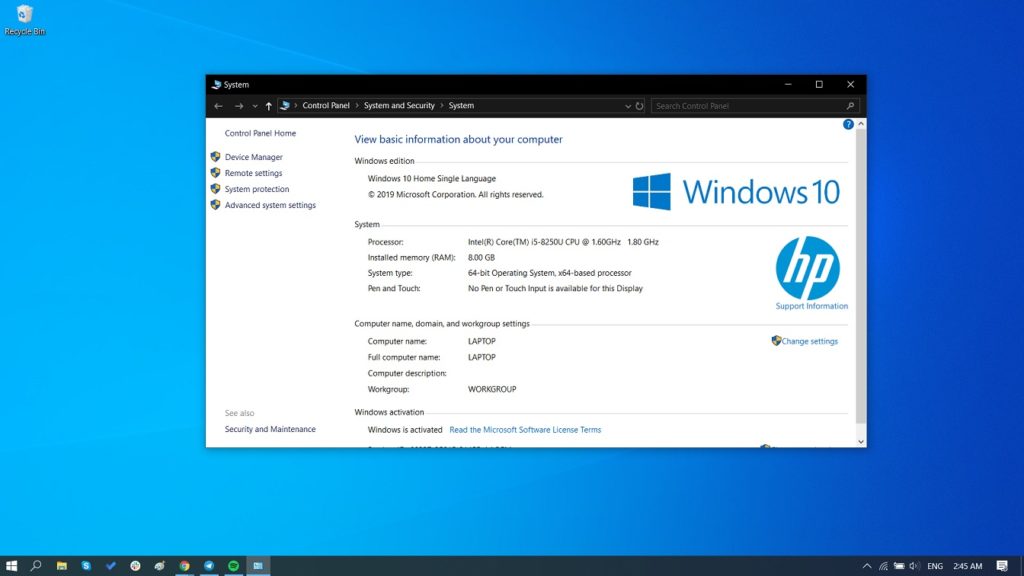
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Powerhouse Within: Understanding Windows 10 CPU Requirements. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!