Harnessing Efficiency: A Guide To CPU Undervolting On Windows 10
Harnessing Efficiency: A Guide to CPU Undervolting on Windows 10
Related Articles: Harnessing Efficiency: A Guide to CPU Undervolting on Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Harnessing Efficiency: A Guide to CPU Undervolting on Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Harnessing Efficiency: A Guide to CPU Undervolting on Windows 10
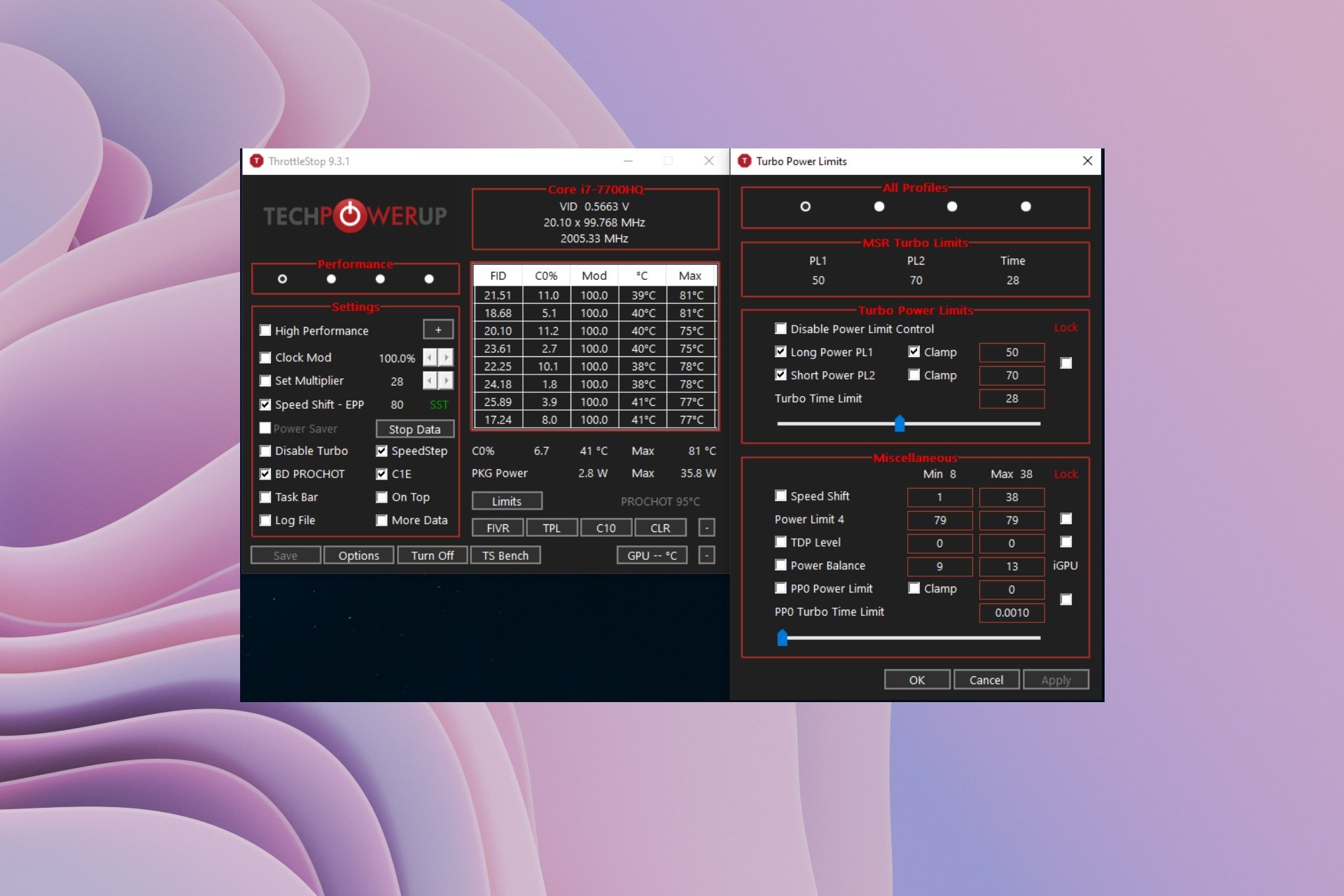
Modern processors, while incredibly powerful, often operate at high voltages, leading to increased heat generation and power consumption. Undervolting, a technique that reduces the voltage supplied to the CPU, presents a compelling solution to mitigate these issues, enhancing both performance and energy efficiency. This guide explores the concept of CPU undervolting on Windows 10, delving into its benefits, methods, and considerations.
Understanding CPU Undervolting: A Deeper Dive
At its core, undervolting involves lowering the voltage supplied to the CPU’s core, a key component responsible for processing data. By reducing the voltage, the CPU consumes less power and generates less heat. This reduction in power consumption translates to lower energy bills and a cooler system, while the decreased heat generation extends the lifespan of the components.
The Potential Benefits of Undervolting
Undervolting offers a myriad of advantages for Windows 10 users:
- Reduced Power Consumption: Lowering the voltage directly translates to lower energy consumption, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint and potentially reducing electricity bills.
- Improved System Stability: A cooler CPU is less prone to thermal throttling, a phenomenon where the processor slows down due to excessive heat. This improved stability can lead to smoother performance and fewer system crashes.
- Enhanced Battery Life: For laptop users, undervolting can significantly extend battery life, allowing them to work or play for longer periods without needing to recharge.
- Quieter System: Lower temperatures often result in quieter fans, creating a more comfortable and less distracting computing environment.
- Extended Component Lifespan: Reduced heat stress on the CPU and other components can prolong their lifespan, leading to a more durable and reliable system.
Undervolting: A Balancing Act
While undervolting offers numerous benefits, it is essential to understand that it is not a universally applicable solution. Over-undervolting can lead to instability or even system crashes, requiring a careful and measured approach.
Methods for Undervolting on Windows 10
Several methods can be employed to undervolt your CPU on Windows 10:
- BIOS/UEFI Settings: Some motherboards offer built-in undervolting options within their BIOS or UEFI settings. This method provides a straightforward and often more stable approach, as it adjusts the voltage at the hardware level.
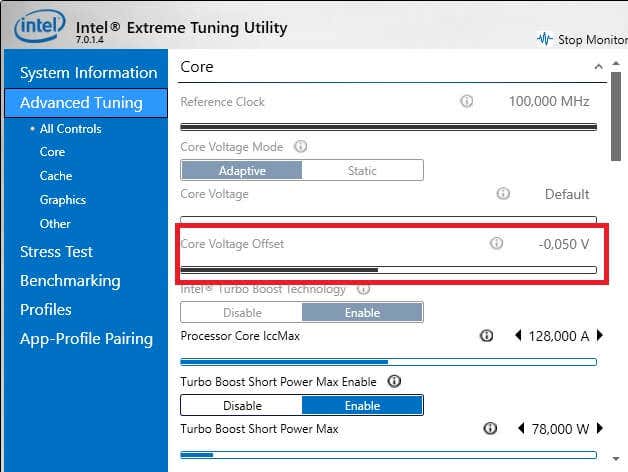
- Software Applications: Dedicated undervolting software applications, such as Intel XTU (for Intel CPUs) or AMD Ryzen Master (for AMD CPUs), allow for precise control over voltage settings. These tools offer a user-friendly interface and advanced features like monitoring and performance tuning.
- Windows Registry Tweaks: Advanced users can modify specific registry keys to adjust the CPU voltage. This method requires a deeper understanding of the system and carries a higher risk of instability if not executed correctly.
Essential Considerations for Undervolting
Undervolting requires careful consideration and a methodical approach to ensure stability and optimal performance. Keep these factors in mind:
- CPU Compatibility: Not all CPUs support undervolting. Check your CPU’s specifications or consult online resources to determine if your model is undervoltable.
- Motherboard Support: Ensure your motherboard has the necessary features and settings to enable undervolting.
- System Stability: Start with small voltage reductions and test your system thoroughly for stability. Monitor system behavior, including performance benchmarks and temperatures, to identify any issues.
- Performance Impact: Undervolting can sometimes lead to a slight performance decrease, especially in demanding applications. Experiment with different voltage levels to find the optimal balance between performance and efficiency.
- Reversibility: Always ensure that your undervolting changes are reversible. This allows you to easily restore the default settings if you encounter any issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about CPU Undervolting
Q: Is undervolting safe for my CPU?
A: Undervolting is generally safe when performed correctly. However, over-undervolting can lead to instability or even damage the CPU. It’s crucial to start with small voltage reductions and monitor your system closely.
Q: Will undervolting affect my CPU’s performance?
A: Undervolting can sometimes lead to a slight performance decrease, especially in demanding applications. However, the performance gain from reduced power consumption and improved stability can often outweigh this minor reduction.
Q: Can I undervolt my CPU if I have a laptop?
A: Yes, you can undervolt your CPU on a laptop, but it may be more challenging than on a desktop PC. Some laptop manufacturers offer undervolting options in their BIOS or through dedicated software applications.
Q: How do I know if my CPU is undervolted?
A: You can monitor your CPU voltage using software applications like HWMonitor or CPU-Z. Compare the current voltage to the default voltage listed in your CPU’s specifications.
Q: Can I undervolt my GPU?
A: Yes, you can also undervolt your GPU, which can offer similar benefits as undervolting the CPU. However, the process and considerations may differ slightly.
Tips for Undervolting Your CPU on Windows 10
- Start with small voltage reductions: Begin with a small undervolt (e.g., 0.05 volts) and gradually increase it until you find the optimal balance between performance and stability.
- Monitor system behavior: Keep a close eye on your system’s temperature, performance, and stability after undervolting. Use monitoring software to track these metrics.
- Run stress tests: Utilize stress testing software to simulate demanding workloads and ensure your system remains stable under stress.
- Backup your system: Before making any significant changes to your system, create a backup of your data and system settings.
- Consult online resources: Explore online forums and communities dedicated to undervolting for specific guidance and troubleshooting tips.
Conclusion
CPU undervolting offers a compelling approach to enhance the performance and efficiency of your Windows 10 system. By reducing power consumption and heat generation, undervolting can lead to a cooler, quieter, and more stable computing experience. However, it’s essential to proceed cautiously, starting with small voltage reductions and carefully monitoring system behavior. With a methodical approach, undervolting can unlock a range of benefits for your Windows 10 system, making it a valuable technique for power users and enthusiasts seeking to optimize their computing experience.
![How to Undervolt CPU Safely [Step-by-Step Guide 2024]](https://10scopes.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/how-to-undervolt-cpu.png)



![How to Undervolt CPU Safely [Step-by-Step Guide 2024]](https://10scopes.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/bios-ez-mode.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Harnessing Efficiency: A Guide to CPU Undervolting on Windows 10. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!