Exploring The Inner Workings Of The Windows 10 Video Player: A Frame-by-Frame Examination
Exploring the Inner Workings of the Windows 10 Video Player: A Frame-by-Frame Examination
Related Articles: Exploring the Inner Workings of the Windows 10 Video Player: A Frame-by-Frame Examination
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Inner Workings of the Windows 10 Video Player: A Frame-by-Frame Examination. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Inner Workings of the Windows 10 Video Player: A Frame-by-Frame Examination
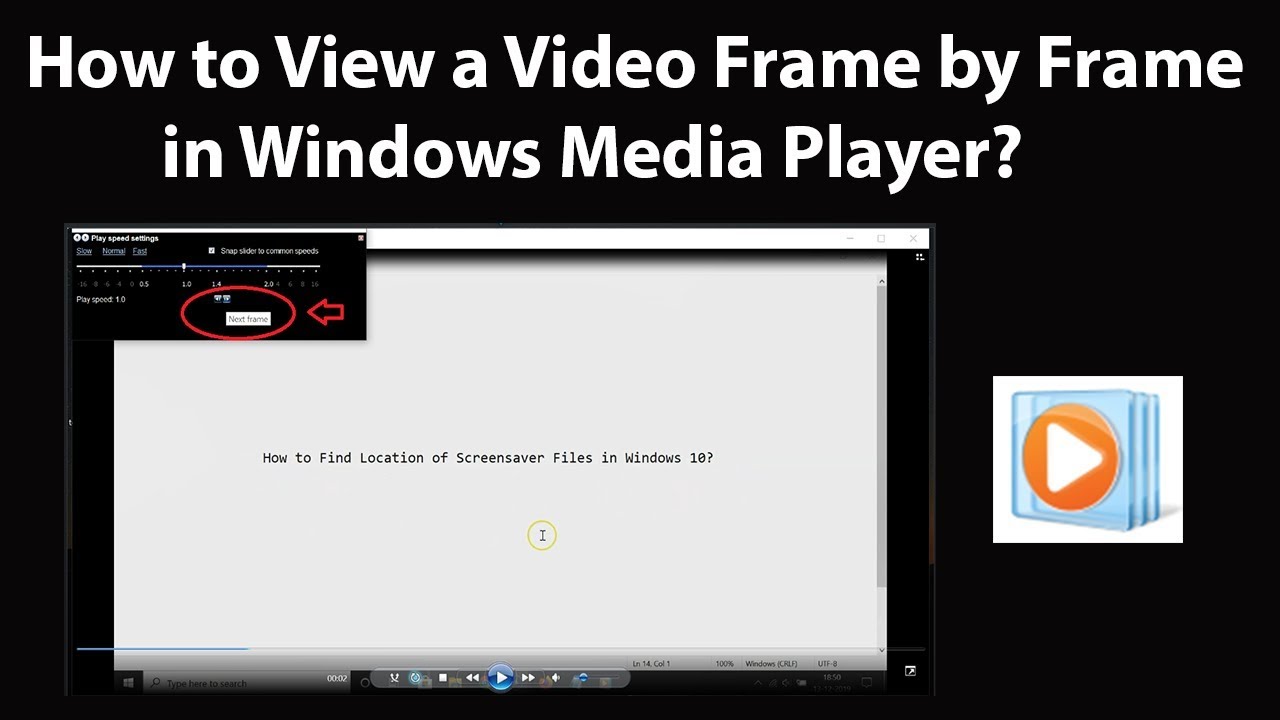
The Windows 10 video player, often referred to as the "Movies & TV" app, provides a user-friendly interface for enjoying a wide range of video content. While its simplicity is appealing, understanding the underlying mechanisms that bring videos to life can enrich the viewing experience and offer valuable insights for troubleshooting and optimization. This article delves into the intricate process of video playback within the Windows 10 video player, analyzing each stage from the initial file retrieval to the final display on the screen.
1. File Retrieval and Decoding:
The journey begins with the selection of a video file. The Windows 10 video player supports a diverse range of formats, including MP4, AVI, MKV, and WMV, among others. Once a file is chosen, the player retrieves the data from the storage location, whether it be a local drive, a network share, or a cloud storage service.
Simultaneously, the player initiates the decoding process. Video files are typically compressed to reduce file size, employing various codecs like H.264, MPEG-4, or VP9. The player utilizes built-in decoders or relies on third-party codecs installed on the system to convert the compressed data back into its original form, enabling playback.
2. Frame Extraction and Presentation:
The decoded video data is then separated into individual frames, each representing a snapshot in time. These frames are arranged in chronological order, forming a continuous sequence that creates the illusion of motion when played back at a specific frame rate.
The Windows 10 video player employs a mechanism known as "video rendering" to display these frames on the screen. The rendering process involves converting the individual frames into a format compatible with the display device, adjusting for factors like resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.
3. Synchronization and Buffering:
To ensure smooth playback, the Windows 10 video player employs a sophisticated synchronization system. The player maintains a buffer, storing a certain number of frames in advance. This buffer acts as a reservoir, ensuring that the player always has a sufficient supply of frames available for display, even if the decoding process experiences occasional delays.
The synchronization process also handles audio playback, ensuring that the audio and video tracks remain perfectly aligned. This alignment is crucial for creating an immersive and enjoyable viewing experience.
4. User Interface and Controls:
The Windows 10 video player provides a user-friendly interface with intuitive controls for managing playback. Users can easily pause, resume, fast-forward, rewind, and adjust the volume. The player also offers additional features like subtitles, playback speed adjustments, and screen aspect ratio settings.
These controls provide users with granular control over their viewing experience, allowing them to customize playback to suit their preferences and viewing conditions.
5. Performance Optimization and Resource Management:
The Windows 10 video player is designed to optimize performance and minimize resource consumption. The player dynamically adjusts its frame rate and buffering strategy based on available system resources, ensuring smooth playback even on less powerful devices.
The player also employs techniques like "frame skipping" and "adaptive bitrate streaming" to reduce the demand on system resources, particularly when dealing with high-resolution or high-bitrate video files.
6. Advanced Features and Capabilities:
Beyond basic playback, the Windows 10 video player offers advanced features that enhance the viewing experience. These features include:
- Subtitle support: The player supports a variety of subtitle formats, allowing users to enjoy videos with translated captions or closed captions.
- Playback speed adjustment: Users can adjust the playback speed to suit their preferences or to accommodate specific content, such as educational videos or audiobooks.
- Screen aspect ratio settings: The player allows users to choose the aspect ratio that best fits their display, preventing letterboxing or pillarboxing.
- Audio output options: The player supports various audio output devices, enabling users to enjoy video content through headphones, speakers, or external audio systems.
Understanding the Importance of Frame-by-Frame Analysis:
Analyzing the video player’s frame-by-frame operation provides several benefits:
- Troubleshooting playback issues: By understanding the individual stages of video playback, users can pinpoint potential causes of issues like stuttering, buffering problems, or audio-video desynchronization.
- Optimizing performance: Knowledge of the player’s resource management strategies can help users optimize system settings and allocate resources effectively for smoother playback.
- Enhancing the viewing experience: Understanding the underlying mechanisms behind video playback can provide a deeper appreciation for the complex processes involved in bringing video content to life.
FAQs about the Windows 10 Video Player Frame-by-Frame Operation:
Q: What happens if the video player cannot decode a specific codec?
A: If the player lacks the necessary codecs, it may display an error message or attempt to use a fallback codec, potentially resulting in lower quality or distorted video. Installing the required codec can resolve this issue.
Q: How does the player handle videos with different frame rates?
A: The player adjusts its output frame rate to match the display device’s refresh rate, ensuring smooth playback. In cases where the video frame rate and display refresh rate differ significantly, the player may introduce slight frame drops or interpolation to maintain a consistent viewing experience.
Q: What factors affect the player’s buffering strategy?
A: The buffering strategy is influenced by factors like network bandwidth, video bitrate, and available system resources. The player dynamically adjusts the buffer size to optimize playback and minimize buffering delays.
Tips for Optimizing Video Playback with the Windows 10 Video Player:
- Ensure sufficient system resources: Close unnecessary applications and ensure ample RAM and processing power for smooth playback.
- Use a reliable internet connection: For online video streaming, a stable and high-speed internet connection is crucial for uninterrupted playback.
- Install the latest video codecs: Keep your system updated with the latest codecs to support a wider range of video formats.
- Adjust playback settings: Experiment with playback speed, aspect ratio, and subtitle settings to optimize the viewing experience.
- Consider using a dedicated video player: For advanced features or specific video formats, consider using a third-party video player with more extensive capabilities.
Conclusion:
The Windows 10 video player, despite its user-friendly interface, relies on a complex and intricate series of processes to deliver a smooth and enjoyable viewing experience. Understanding these processes, from file retrieval and decoding to frame presentation and resource management, provides valuable insights into the technical aspects of video playback and empowers users to troubleshoot issues, optimize performance, and enhance their overall viewing experience.





![[Updated 2024] Top 8 Video Player with Frame by Frame Function - EaseUS](https://recorder.easeus.com/images/en/screen-recorder/resource/video-player-with-frame-by-frame.jpg)
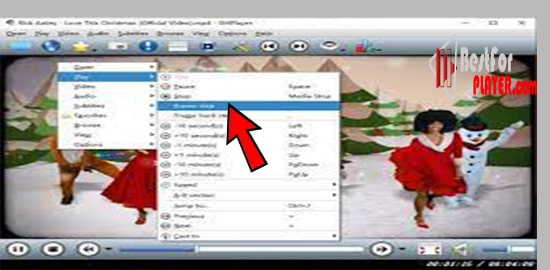
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Inner Workings of the Windows 10 Video Player: A Frame-by-Frame Examination. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
