Dual Booting Windows 10 And Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
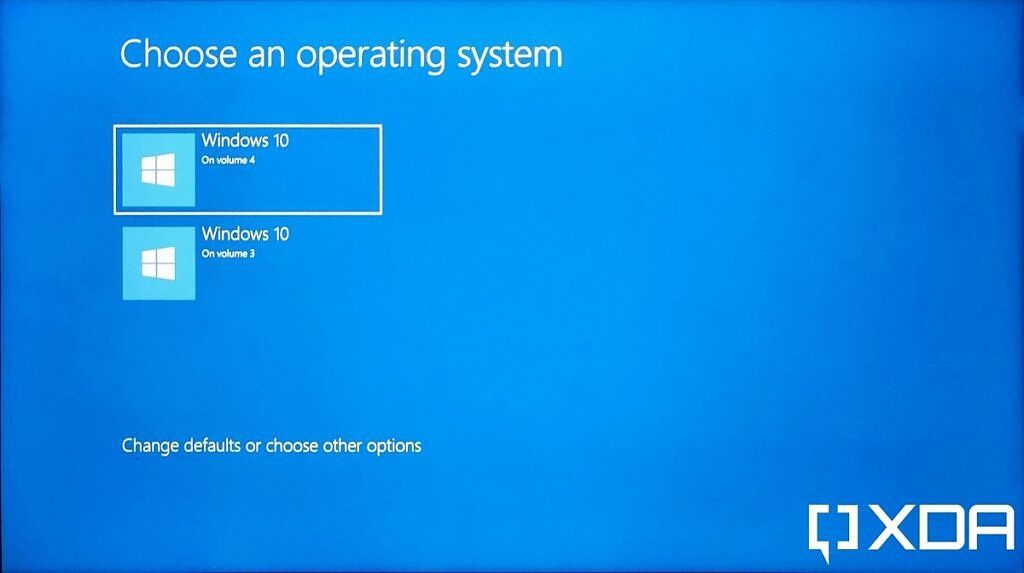
The decision to install both Windows 10 and Windows 11 on a single computer is a strategic one, driven by various factors such as compatibility concerns, program preferences, or a desire to explore the latest operating system while retaining the familiarity of a previous version. This guide will explore the intricacies of dual booting these two operating systems, highlighting the advantages and challenges involved, and providing practical advice for successful implementation.
Understanding the Concept of Dual Booting
Dual booting, as the name suggests, involves configuring a computer to run two or more operating systems independently. When the system is powered on, the user is presented with a boot menu, allowing them to select the desired operating system. Each operating system maintains its own files, settings, and applications, operating in isolation from the others.
Why Choose Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11?
Several compelling reasons motivate users to consider dual booting Windows 10 and Windows 11:
- Software Compatibility: Some applications and games may not be compatible with the latest operating system, Windows 11. Dual booting allows users to access these programs on Windows 10 while enjoying the features of Windows 11 for other tasks.
- Performance Optimization: Windows 11, with its new features and enhanced security, can demand more resources. Dual booting allows users to switch to Windows 10 for resource-intensive tasks, ensuring smooth performance.
- Exploring New Features: Dual booting provides a safe environment to experiment with Windows 11 without affecting the stable and familiar environment of Windows 10.
- System Stability: If Windows 11 encounters issues or instability, users can seamlessly switch to Windows 10, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted productivity.
Prerequisites for Dual Booting
Before embarking on the dual boot process, ensure that the following requirements are met:
- Sufficient Storage Space: Allocate enough hard drive space for both operating systems. A minimum of 50 GB is recommended for each operating system.
- Backup Data: Create a complete backup of all important data before proceeding. This safeguards against accidental data loss during the installation process.
- Understanding Partitioning: Dual booting requires partitioning the hard drive to create separate storage areas for each operating system. Familiarity with basic disk management concepts is beneficial.
- Installation Media: Obtain installation media for both Windows 10 and Windows 11, either as a USB drive or DVD.
Installing Windows 10 and Windows 11 in Dual Boot Mode
The installation process involves the following steps:
- Partitioning the Hard Drive: Use the disk management tool in Windows to create two separate partitions. One partition will be for Windows 10, and the other for Windows 11.
- Installing Windows 10: Boot from the Windows 10 installation media and follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows 10 on the dedicated partition.
- Installing Windows 11: After installing Windows 10, boot from the Windows 11 installation media and install it on the other partition.
- Setting Boot Order: Access the BIOS settings and adjust the boot order to prioritize the desired operating system. This ensures that the chosen operating system loads automatically at startup.
Managing Dual Boot Systems
Once both operating systems are installed, it’s essential to manage their coexistence effectively:
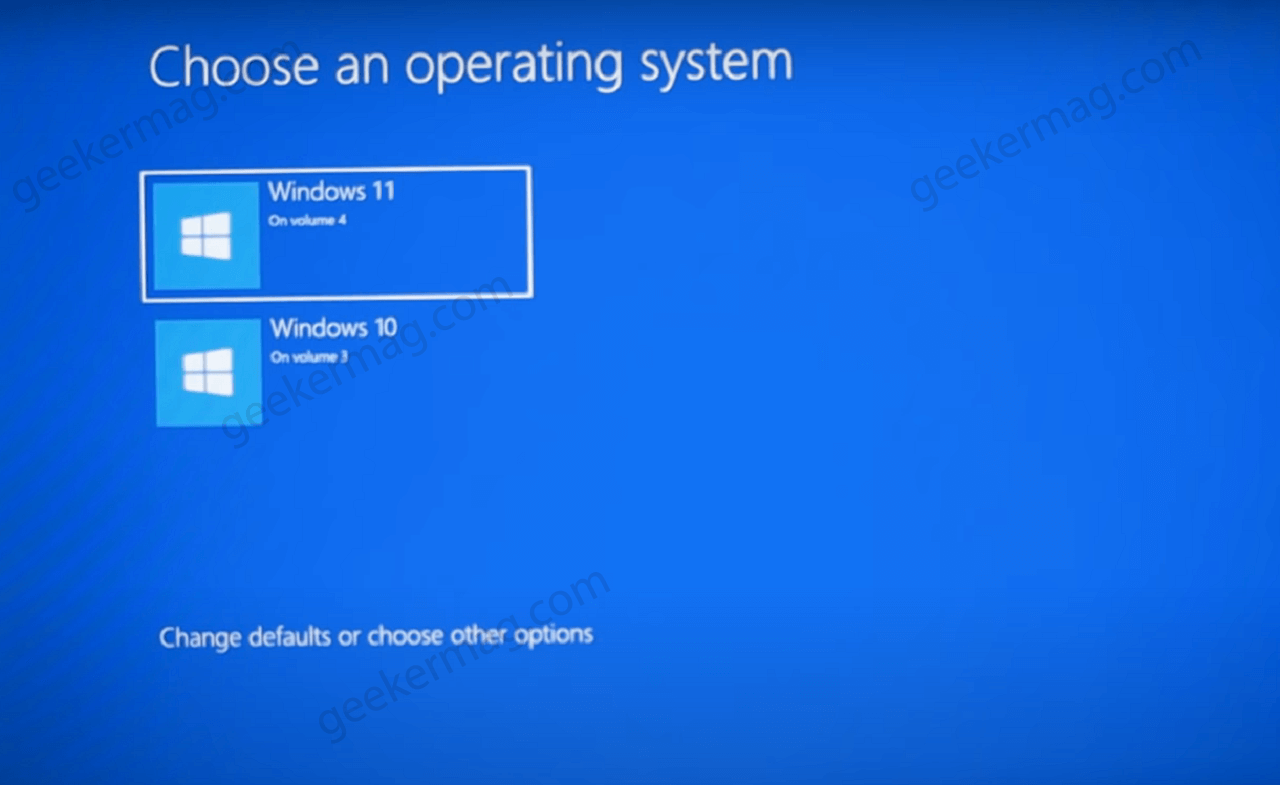
- Boot Menu: The boot menu, typically accessed by pressing a specific key during startup (usually F12 or Esc), provides the option to select the desired operating system.
- File Sharing: Sharing files between the two operating systems can be accomplished using a shared network drive or by connecting external storage devices.
- Updating Both Systems: Keep both operating systems updated with the latest security patches and software updates to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Troubleshooting: If issues arise, consult online resources or contact technical support for assistance.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Dual booting can present challenges, but understanding the potential issues and their solutions can ensure a smooth experience:
- Boot Order Problems: Incorrect boot order can prevent the desired operating system from loading. Re-adjust the boot order in the BIOS settings to resolve this issue.
- Driver Conflicts: Some drivers may not be compatible with both operating systems. Update drivers regularly and consult device manufacturers for compatible versions.
- System Performance: Dual booting can impact system performance, especially if both operating systems are resource-intensive. Optimize system resources by adjusting settings and closing unnecessary applications.
- Storage Space Management: Monitor the storage space allocated to each operating system to avoid disk space limitations.
FAQs about Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11
Q: Can I install Windows 11 first and then Windows 10?
A: Yes, you can install either operating system first. However, it’s generally recommended to install Windows 10 first, as it might be easier to manage the boot order and partitioning process.
Q: Can I upgrade Windows 10 to Windows 11 and keep the dual boot setup?
A: No, upgrading Windows 10 to Windows 11 will overwrite the existing installation, removing Windows 10. To keep both operating systems, a clean installation of Windows 11 on a separate partition is necessary.
Q: Can I use the same user account for both Windows 10 and Windows 11?
A: While you can use the same username, it’s not recommended. Each operating system maintains its own user accounts, settings, and data. Using separate accounts for each operating system ensures a cleaner separation and avoids potential conflicts.
Q: Can I remove one operating system from a dual boot setup?
A: Yes, you can remove an operating system by deleting its partition from the disk management tool. However, ensure that you have backed up any important data before proceeding.
Tips for Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Use a Separate Hard Drive: If possible, install each operating system on a separate hard drive. This provides better performance and eliminates the need for complex partitioning.
- Choose the Right Partition Size: Allocate enough disk space for each operating system based on its requirements and anticipated usage.
- Create a Recovery Drive: Create a recovery drive for each operating system to assist with troubleshooting and system restoration.
- Keep System Updates Current: Update both operating systems regularly to address security vulnerabilities and improve performance.
Conclusion
Dual booting Windows 10 and Windows 11 offers a flexible approach to managing multiple operating systems on a single computer. While it requires careful planning and execution, the benefits of having both operating systems readily available outweigh the challenges. By understanding the concepts, prerequisites, and potential issues, users can successfully configure and manage their dual boot systems, enjoying the best of both worlds. Whether it’s for software compatibility, performance optimization, or exploring new features, dual booting empowers users to choose the operating system that best suits their needs at any given moment.
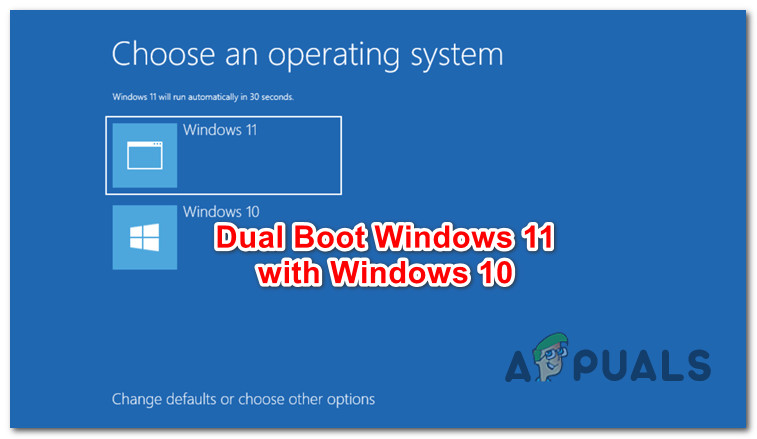
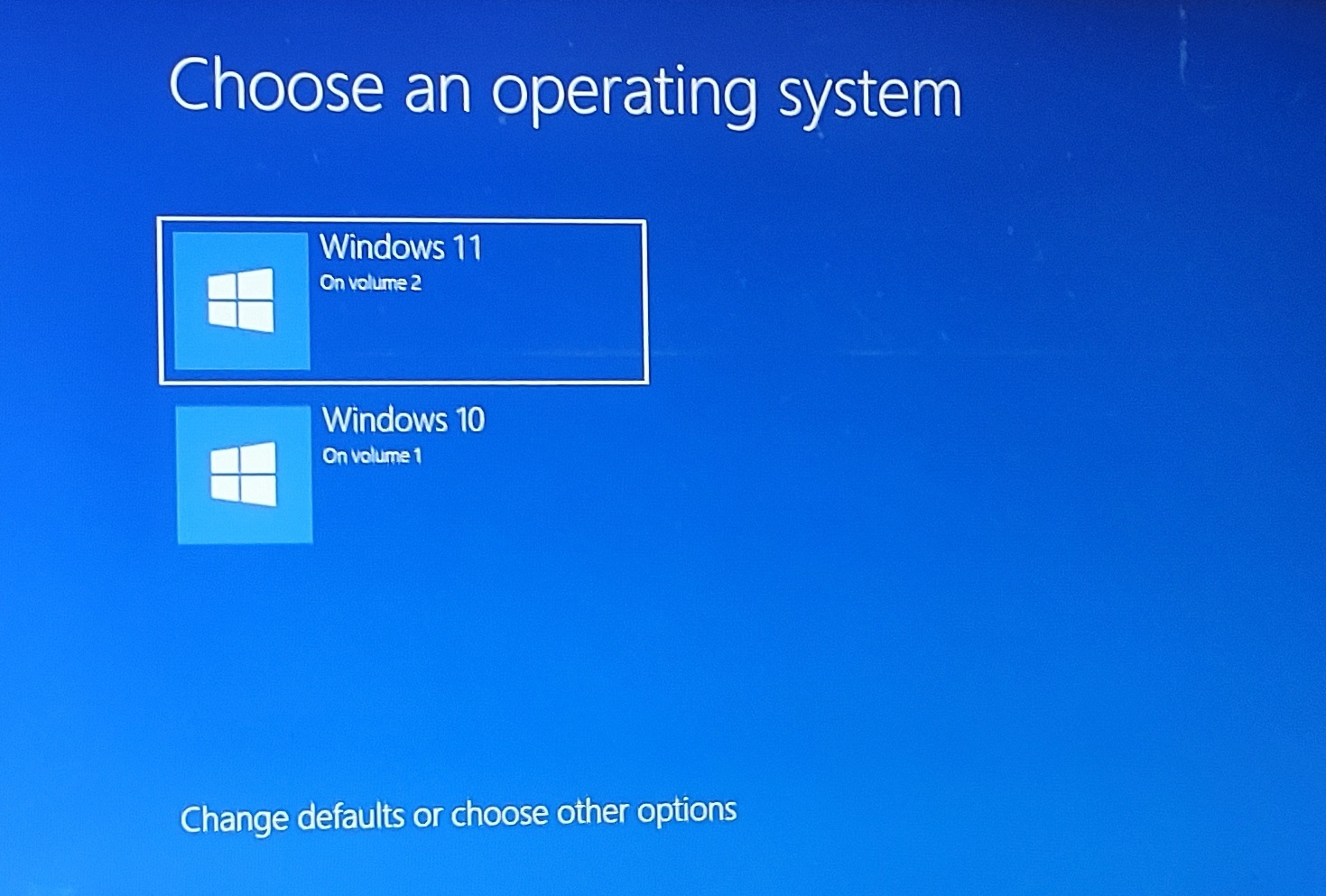



![How To Dual Boot Windows 10 and Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fRm9ztZ9mcc/maxresdefault.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dual Booting Windows 10 and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!